Figure 3.
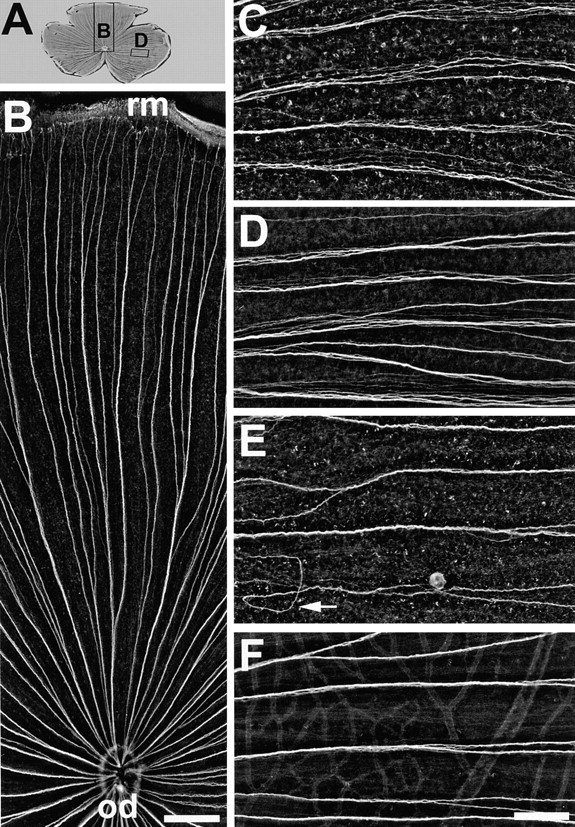
Ig domains 1 and 3 of neurolin contribute to axonal fasciculation in vivo. (A) Wholemount of a retina injected with mAb N100 against Ig domain 3. The positions of B and D are indicated by rectangles. (B) Dorsal segment of the retina in A. The directed growth of young RGC axons along fascicles from the retinal margin (rm) to the optic disk (od) is maintained and is as orderly as in control retinae. In retinae injected with mAb N850 against Ig domain 1 (C) or mAb N100 against Ig domain 3 (D) young RGC axons in fascicles fail to adhere tightly to each other. The distance between neighboring axons is increased compared to controls (F). (E) mAb N518 against domain 2 does not interfere with tight fasciculation, but causes pathfinding errors of young RGC axons (arrow). C–F are from the temporal retina, oriented with the retinal margin to the right, and the optic disk to the left. Bars, B, 300 μm; C–F, 100 μm.
