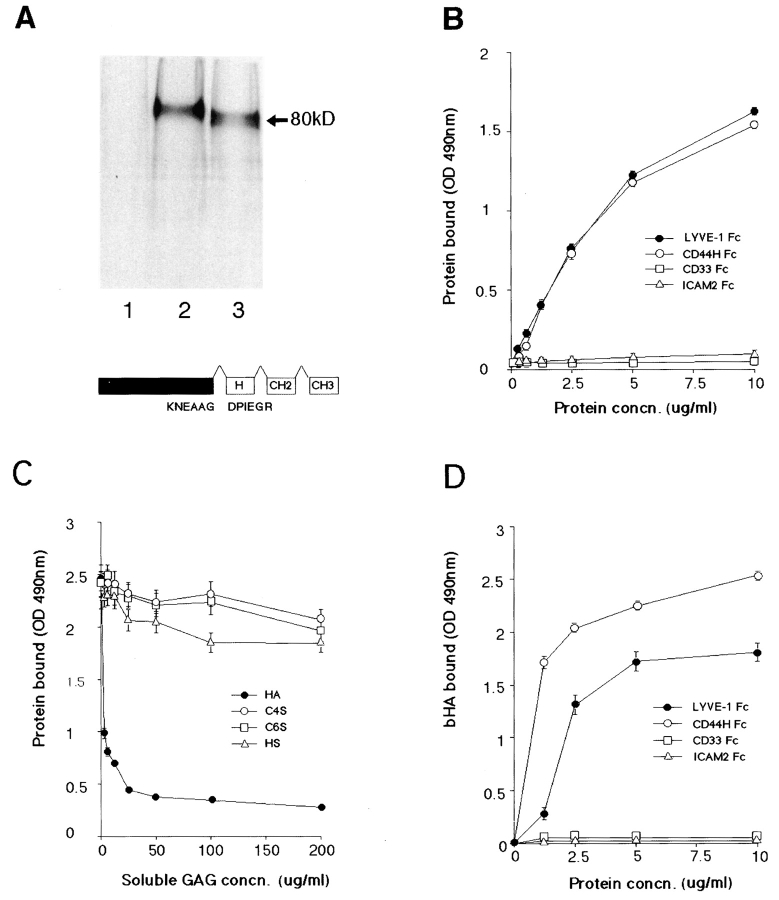
Figure 4.
LYVE-1 binds both immobilized and soluble HA. LYVE-1, expressed as a soluble IgFc fusion protein in transiently transfected human COS fibroblasts, was compared with CD44 for binding to HA and other glycosaminoglycans. A shows LYVE-1 and CD44H Fc fusion proteins isolated from the supernatants of [35S] methionine/cysteine-labeled transfectants and electrophoresed on a 7.5% polyacrylamide SDS-PAGE gel. Samples were the protein A–Sepharose adsorbed proteins from control untransfected cells (lane 1), CD44H Fc transfected cells (lane 2), and LYVE-1 transfected cells (lane 3). The LYVE-1 fusion protein comprises residues 1–232 of the extracellular domain fused to the hinge (H), CH2, and CH3 domains of human IgG1. Details of the CD44H Fc protein, which includes residues 1–200 of the extracellular domain, have been published previously (1). For ligand binding assays, LYVE-1 Fc was compared with CD44H Fc and the negative control fusion proteins CD33 Fc and ICAM-2 Fc for adhesion to immobilized and soluble HA in 96-well microtiter plates (see Materials and Methods). B shows binding of the fusion proteins to immobilized HA, in the absence of competing glycosaminoglycans; C shows binding (LYVE-1 Fc only) in the presence of free chondroitin-4-SO4, chondroitin-6-SO4, or heparin; and D shows binding to soluble biotinylated HA. Detection of bound fusion protein and biotinylated HA was carried out using peroxidase-conjugated anti–human IgFc antibody and peroxidase-conjugated streptavidin, respectively. Values are the mean ± SEM of at least three replicates.