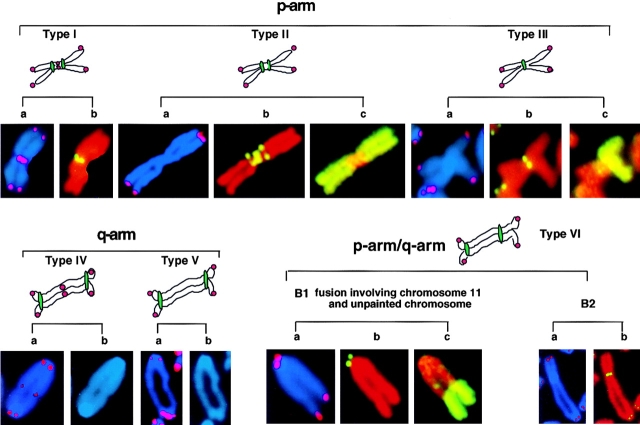
Figure 4.
Examples of the different end-to-end fusions detected in mTER−/− cells. The chromosomal arms involved in the fusion are inferred by the morphology of the fused chromosome. Chromosomes probed with telomeric PNA to characterize the fusion according to the presence or absence of detectable telomeric sequences at the fusion point are depicted in panels a. Chromosomes probed with minor satellite DNA to characterize the fusion according to the number and location of centromeres are depicted in panels b (in p-arm and p-arm/q-arm fusions). Panels b (in q-arm examples) depict DAPI staining of the fusion. Panels c depict chromosome painting with whole- chromosome DNA from chromosome 2 (example of type II fusion) and chromosome 11 (examples of type III fusion and p-arm/q-arm fusion). Chromosomes are counterstained with DAPI for telomere probe and propidium iodide for minor satellite and chromosome probes.