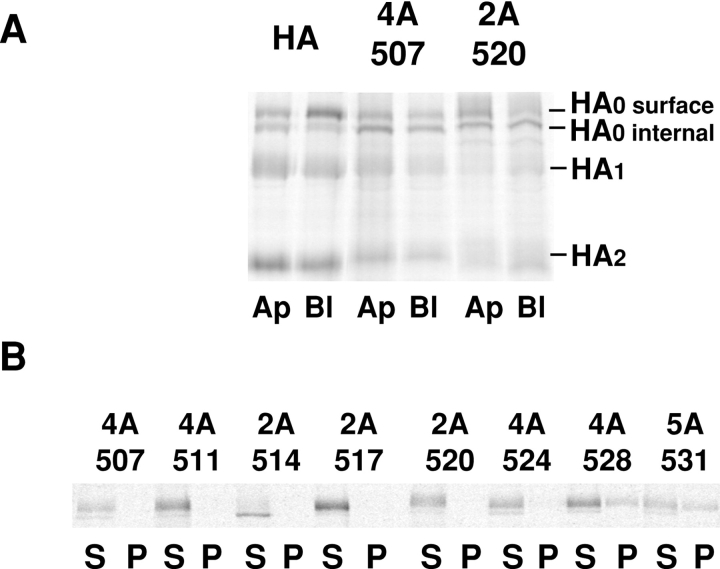
Figure 2.
Mutations in the HA TM affect transport to the apical cell surface and solubility in Triton X-100. (A) MDCK monolayers expressing the HA types shown were grown on filter culture inserts for 5 d and then subjected to a pulse-chase protocol in which trypsin was present during the chase in either the apical (Ap) or basolateral (Bl) compartment. After the chase, HAs were immunoprecipitated, separated by PAGE, and then analyzed by a PhosphorImager. A representative image comparing HA and two mutants is shown. (B) MDCK cells expressing the mutants shown were pulse-labeled and chased for 40 min, then the cells were lysed in 1% Triton X-100 on ice. The cell lysate was centrifuged in a microfuge and separated into supernatant (S) and pellet (P) fractions. HA was immunoprecipitated from each fraction and analyzed as in A.