Figure 2.
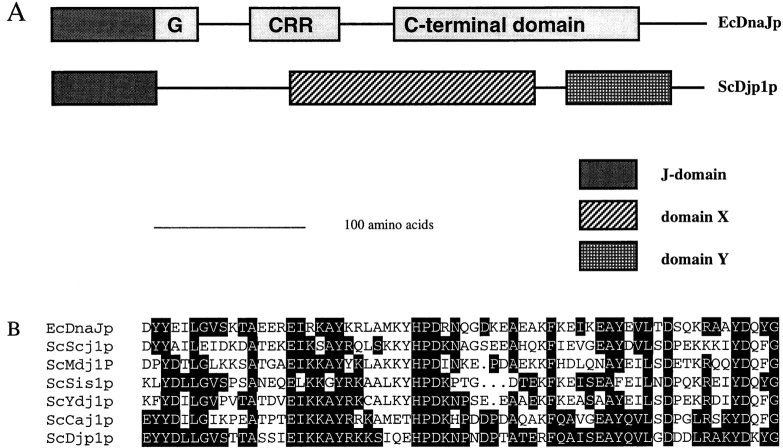
Djp1p is a member of a novel subfamily of J-domain– containing proteins. (A) Schematic representation of the modular structure of Djp1p compared with E. coli DnaJ. According to the ProDom database (Gouzy et al., 1996), which makes use of the domainer algorithm (Sonnhammer and Kahn, 1994), Djp1p consists of three conserved domains. It belongs to a subfamily of J-domain–containing proteins with a modular organization different from that of other DnaJ homologues. The typical G domain, cysteine-rich region (CRR) and COOH-terminal domain are absent. Instead, two conserved blocks of amino acids are observed. Block X (Domain ID: 8587, Prodom34) consists of ∼170 amino acid residues and has been found in Djp1p (sw P40564), Caj1p (Mukui et al., 1994; sw P39101), and Yay1p (sw Q10209). Block Y (Domain ID: 7042, Prodom34) has been found in Djp1p, Caj1p, Yay1p, PfRESA1p (sw P13830), and AtDnaJ-like protein (these sequence data are available from GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ under accession number Y11969). (B) Amino acid sequence comparison of the J-domain (Prosite PS00636) of Djp1p with the J-domain of EcDnaJ (sw P08622), and the S. cerevisiae J-domain–containing proteins Scj1p (P25303), Mdj1p (P35191), Sis1p (P25294), Ydj1p (P25491), and Caj1p. Amino acids identical to Djp1p are indicated with black boxes.