Figure 1.
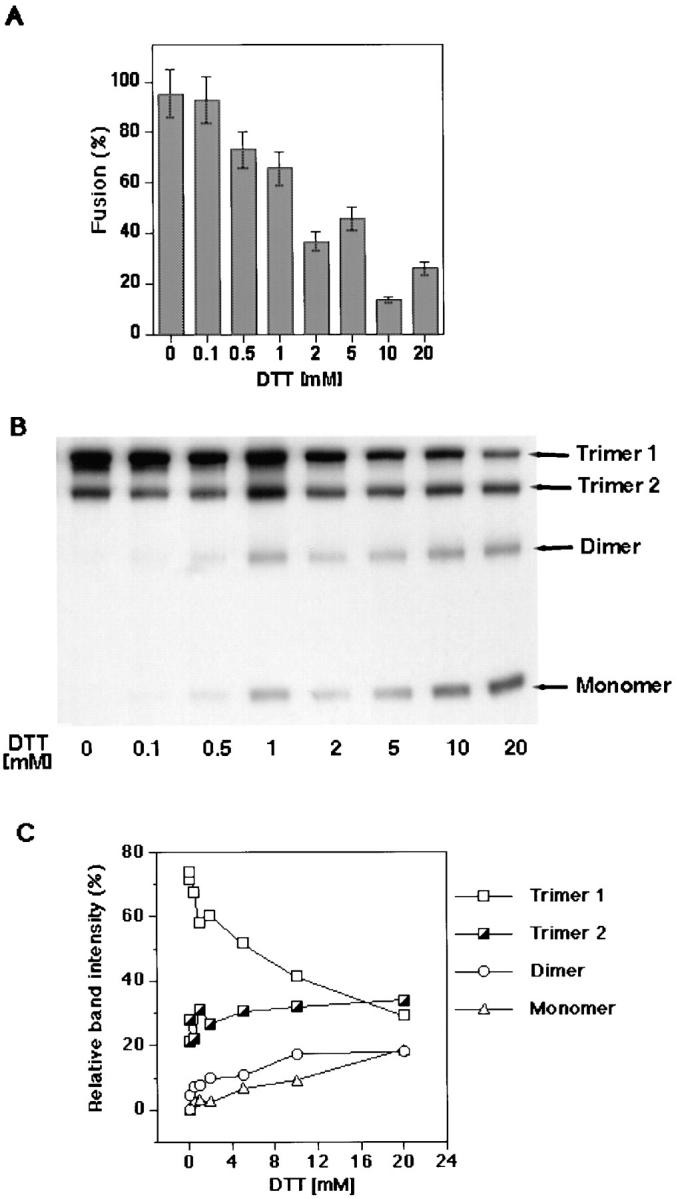
Effects of DTT-dependent disulfide-to-thiol exchange on fusion and gp64 trimerization. (A) Increasing concentrations of DTT significantly inhibited fusion between RBC and gp64-expressing Op1D cells. Op1D cells were treated with 0.1–20 mM DTT for 30 min followed by 15 min alkylation with 10 mM NaIA. PKH26-labeled RBC were then added to Op1D cells and the medium was acidified (i.e., pH 5.1) to trigger the fusion. Each bar represents mean fusion ± SE for 200 cells counted. (B) Western blot analysis of 0.1–20 mM DTT-treated and 10 mM NaIA-alkylated Op1D cells. Cells were lysed in nonreducing 1.5% SDS lysis buffer and proteins were separated by 6% SDS-PAGE. Increasing concentrations of DTT reduced gp64 trimers into monomers and dimers. (C) Quantitative Western blot analysis of DTT-reduced gp64 immunoreactive bands. Relative band intensities, measured by ECF, are presented as a percentage of the total band intensity within the sample lane. DTT caused reduction of mostly trimer 1.
