Figure 1.

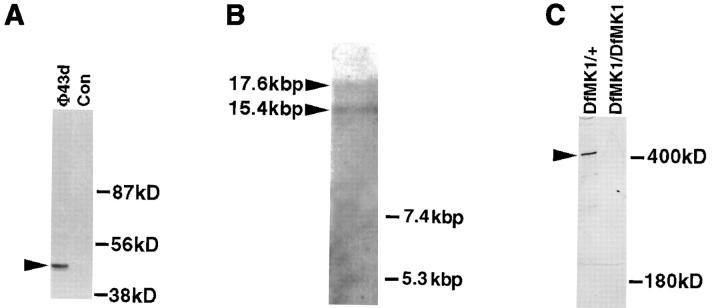
Structural and molecular analysis of kakapo. (A) The specific reactivity of mAb#19 with the expressed protein sequence of the cDNA clone isolated from phage Φ43d (representing the COOH-terminal end of Kak) is demonstrated. The 43d cDNA insert was subcloned in frame to FLAG-tagged–containing vector. This construct was used to transfect 293 human cultured cells, and the extract from the transfected cells was first immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG antibody and then subjected to Western analysis with mAb#19. While mAb#19 reacts with the expected 43-kD polypeptide in the transfected cells (arrowhead in lane Φ43d), it did not react with any band in the control nontransfected cells (Con). (B) Northern blot analysis of poly (A+) RNA prepared from 12–20-h-old embryos. The kak mRNA was detected using a kak cDNA fragment of 4.6 kbp (nucleotides 6394–10993 of the cDNA). RNA molecular marker sizes are shown on the right. kak cDNA probe hybridizes specifically with two transcripts of ∼15.4 and ∼17.6 kbp (arrowheads). (C) Western blot analysis of wild-type (Df(2R)MK1/+) or mutant (Df(2R)- MK1/Df(2R)MK1) embryos with anti-Kak polyclonal antibody. Each lane represents extract made from 30 embryos (stages 16– 17). Mutant embryos were selected according to their phenotype. The anti-Kak antibody recognizes a specific band of ∼400 kD. We used as markers (shown on the right) the Drosophila laminin A chain (∼400 kD) and standard molecular mass markers (only the ∼180 kD size is shown). The specificity of the polyclonal antibody is indicated by its lack of reactivity with extracts from embryos homozygous for Df MK1. (D) The deduced amino acid sequence of Kak. The 4,151–amino acid sequence was derived from the single ORF in the 12,989-nucleotide cDNA sequence. The sequence presented lacks an initiator methionine. kak ORF terminates at position 12454 and is followed by a putative polyadenylation signal at position 12979. The amino acid residue number is indicated to the right of each line. Leucine residues in potential Leucine-zipper domains are in bold text. Kakapo repeats are delineated with bent arrows and are numbered. The presented sequence data are available from EMBL nucleotide sequence database under accession number Y09430. (Note: All the amino acid positions indicated in this paper refer to the amino acid sequence presented in Fig. 1 D, which does not include the two alternative NH2-terminal spliced forms described in Gregory and Brown, 1998.)