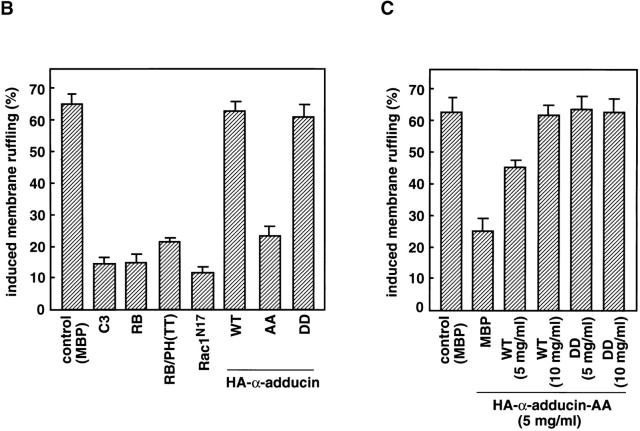
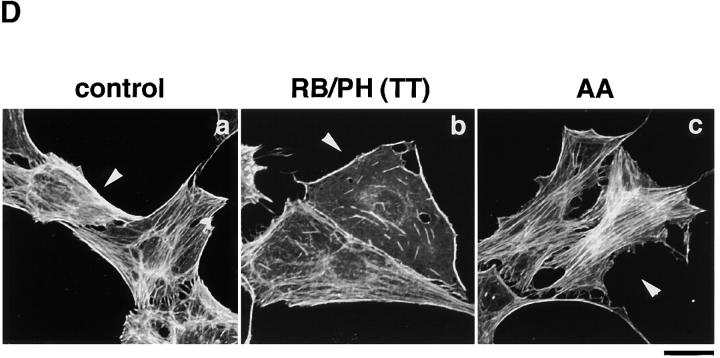
Figure 5.
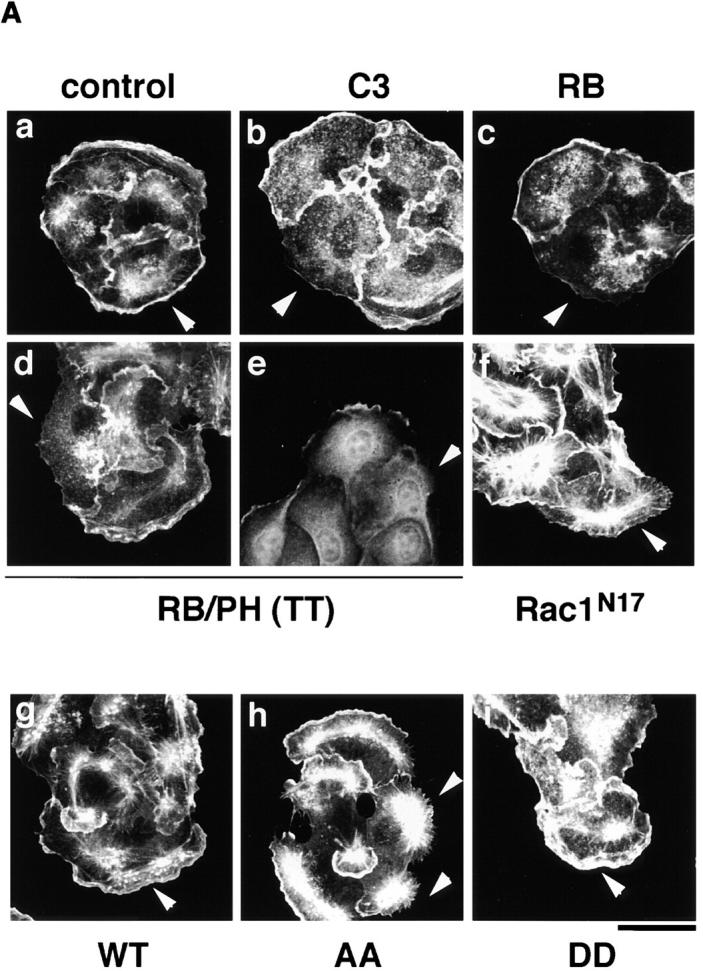
The inhibition of the TPA-induced membrane ruffling by the mutants of Rho-kinase and α-adducin. (A) The serum-deprived MDCK cells were microinjected with MBP (2 mg/ ml; panel a), C3 (0.1 mg/ml; panel b), GST-RB (2 mg/ml; panel c), MBP-RB/ PH (TT) (2 mg/ml; panels d and e), or Rac1N17 (0.2 mg/ml; panel f), HA-α-adducin (WT) (5 mg/ml; panel g), HA-α-adducin-AA (5 mg/ml; panel h), or HA-α-adducin-DD (5 mg/ml; panel i) along with a marker protein (rabbit or mouse IgG, 0.5 mg/ml). After a 30-min incubation, the cells were stimulated with 200 nM TPA for 15 min. F-actin (panels a–d and f–i) and Thr445-phosphorylated α-adducin (panel e) were visualized. Arrowheads indicate the microinjected cells. Bar, 25 μm. (B) The ratios of the membrane ruffling–induced cells to the cells injected with proteins described in A are indicated. Data are means ± SEM of triplicate determinations. (C) Specificity of the effect of HA-α-adducin-AA on the TPA-induced membrane ruffling. HA-α-adducin-AA (5 mg/ml) was microinjected along with indicated proteins. The ratios of the membrane ruffling–induced cells to the injected cells are indicated. Data are means ± SEM of triplicate determinations. (D) HA-α-adducin-AA had no effect on stress fiber formation. The serum-deprived NIH3T3 cells were microinjected with MBP (2 mg/ml; panel a), MBP-RB/PH (TT) (2 mg/ml; panel b), or HA-α-adducin-AA (5 mg/ml; panel c). After a 30-min incubation, the cells were stimulated with 50 ng/ml LPA for 20 min. F-actin was visualized. Arrowheads indicate the microinjected cells. Bar, 10 μm. These results are representative of three independent experiments.