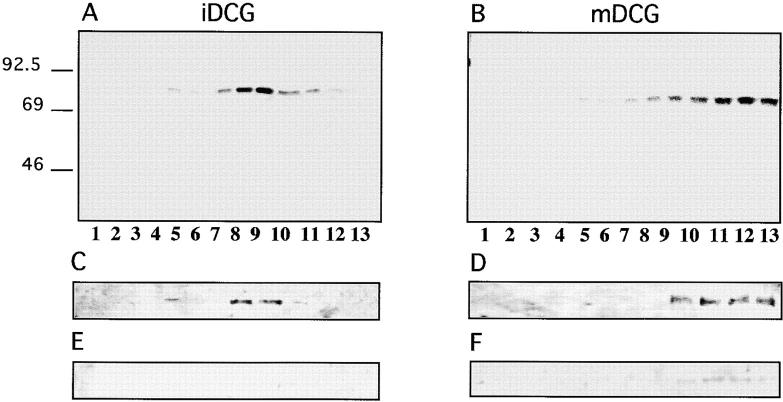
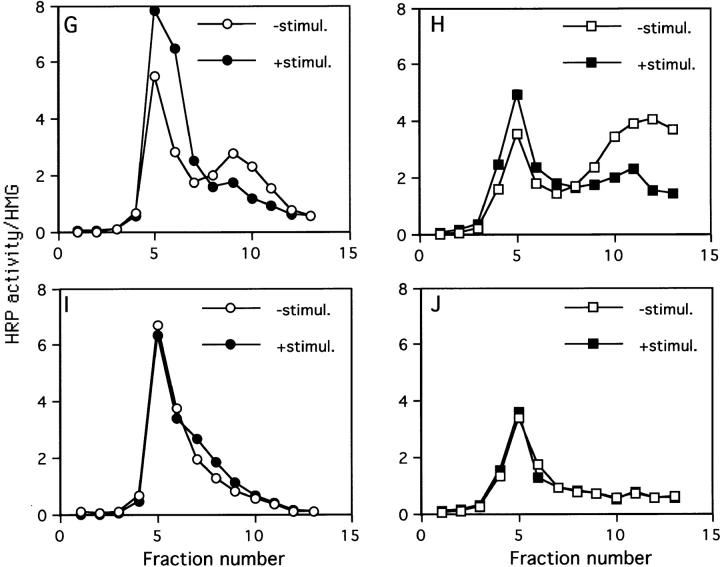
Figure 4.
Sorting of SgII, ssHRPP-selectin, and ssHRPP-selectinY777A to iDCG and mDCG. (A and B) PC12 cells expressing ssHRPP-selectin were pulsed for 10 min at 37°C with 35S-labeling mix and chased for 20 min at 37°C (A) or for 16 h (B) at 37°C to label iDCG or mDCG, respectively. The PNS obtained from these cells was centrifuged on initial 0.3–1.2 M sucrose velocity gradients followed by recentrifugation of fractions corresponding to iDCG or mDCG on 0.9–1.7 M sucrose equilibrium gradients as described in Materials and Methods. After fractionation, 200 μl of each fraction was diluted with NDET buffer and immunoprecipitated with anti-SgII. The samples were then separated by 10% SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, dried, and exposed to a PhosphorImager screen (Bio-Rad Laboratories). Alternatively, cells expressing ssHRPP-selectin (C–H) or ssHRPP-selectinY777A (I and J) were stimulated with 10 mM Carbachol for 30 min at 37°C (E, F, G •, H ▪, I •, and J ▪), or incubated without secretagogue (C, D, G ○, H □, I ○, and J □) and subjected to the two-step fractionation procedure for separation of iDCG and mDCG, as described in the legend for A and B. After fractionation, aliquots of each fraction were separated by SDS-PAGE followed by Western blotting using anti-SgII followed by 125I–protein A (C–F) or used for measurement of HRP activity normalized to that in the homogenate (G–J).