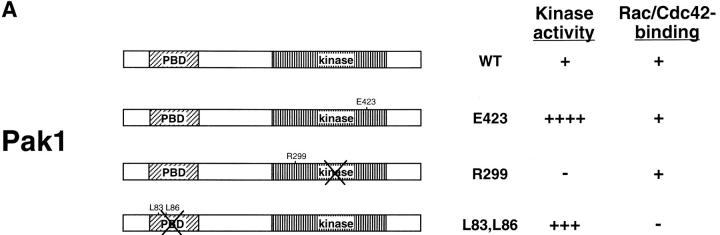
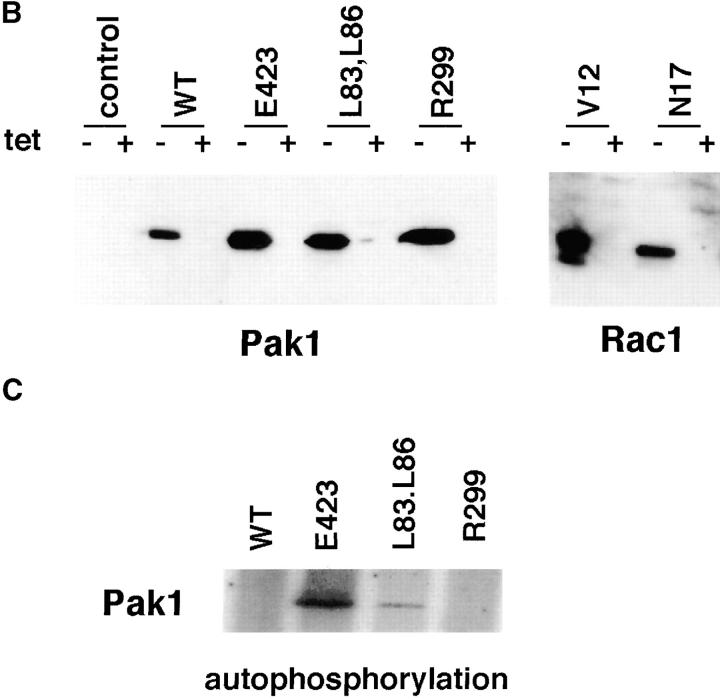
Figure 1.
Tetracycline regulated expression of various forms of Pak1 and Rac1 in NIH-3T3 clonal cell lines. (a) Structure and activities of Pak1 and Rac1 mutants used in this study. A diagrammatic representation of the wild-type and mutant forms of Pak1 and Rac1 are shown in the top panel with amino acid changes denoted by a single letter amino acid abbreviation of the mutant residue. For Pak1, domains shown include the p21 binding domain (PBD) and the catalytic domain (kinase). (b) Inducible expression of Pak1 and Rac1 proteins. S2-6 NIH-3T3 cells, containing the tTA transactivator, were transfected with tetracycline-regulatable expression plasmids bearing either no insert (control), or various forms of HA epitope–tagged Pak1 or Myc-tagged Rac1. Pak1 constructs: wild-type, WT; constitutively activated, E423; kinase-inactive, R299; constitutively activated and Cdc42/Rac-binding defective, L83,L86. Rac1 constructs: constitutively activated, V12; and dominant-negative, N17. Stable clones were isolated and characterized in both the presence and absence of tetracycline (tet) for Pak1 expression by immunoblot with anti-HA antisera, and for Rac1 expression by immunoblot with anti-Myc antisera. (c) Protein kinase activity of induced cell lines. HA-tagged Pak1 was immunoprecipitated from the indicated cell lines and tested for auto-kinase activity.