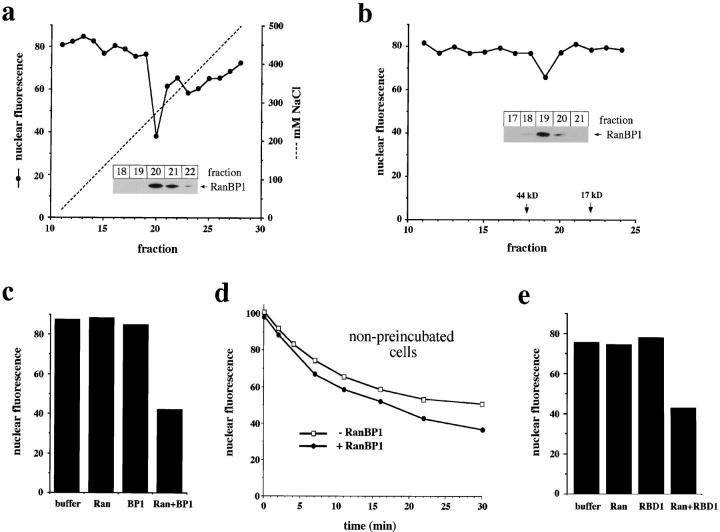
Figure 4.
RanBP1 and RanBP1-related domains promote nuclear export in vitro. (a) Activity profile of Mono Q fractions. HeLa cytosol was chromatographed on a Mono Q ion exchange column. 20 μl of individual fractions was dialyzed against transport buffer and added to nuclear export reactions. (b) Activity profile of Superdex 200 fractions. Nuclear export reactions contained 25 μl of Superdex 200 fractions. (a and b) All reactions contained 25 μg/ml Ran. (Insets) Immunoblots of indicated fractions to detect RanBP1. RanBP1 was not detected in any other fraction. (c and e) Stimulation of nuclear export by RanBP1 (c) and RBD1 (amino acids 1155–1321) of RanBP2 (e). Reactions contained 25 μg/ml Ran, 25 μg/ml RanBP1, and 7.5 μg/ml RBD1 as indicated. (d) Time course of nuclear export in the absence (□) or presence (•) of 15 μg/ml RanBP1 using cells that have not been preincubated with RanQ69L. (a–c, and e) RanQ69L cc-NES–preincubated cells were used in all reactions.