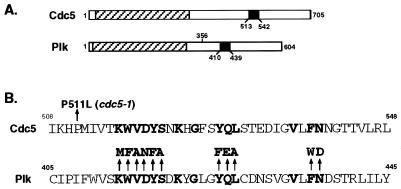
Figure 1.
(A) Structures of Cdc5 and Plk. A hatched box denotes the kinase domain, and a closed box denotes the polo-box. Plk lacking the C-terminal domain (PlkΔC) has lost amino acid residues 356 to 604. (B) Identification of the cdc5–1 mutation site and diagram showing the polo-box mutants generated in Plk. Yeast genomic DNAs prepared from the cdc5–1 mutant (H5C1A1) and its parental wild-type strain (H4939–1b) (a gift of L. Hartwell, University of Washington) were used as templates to amplify full length cdc5–1 and CDC5 genes, respectively, by using the PCR. Restriction and complementation analyses confirmed the cloned genes (data not shown). DNA sequence analysis revealed a point mutation (conversion of Pro511 to Leu) in the cdc5–1 allele. Introduction of the P511L mutation into the wild-type Cdc5 was sufficient to abolish its capacity to complement the cdc5–1 defect (data not shown). Conserved amino acids among all of the polo family members known to date are in bold letters; arrows point to amino acids changed in the point mutations.