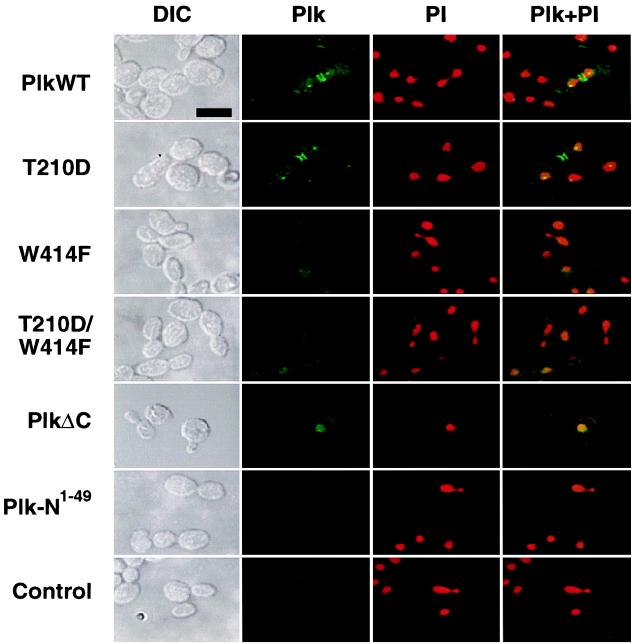
Figure 4.
The requirement of the polo-box for Plk localization. To localize wild-type and mutant forms of Plk in a diploid wild-type strain, 1788, EGFP–Plk fusion constructs were generated and expressed under the control of the GAL1 promoter. Transformants expressing EGFP fusion constructs were stained with propidium iodide to visualize chromosomal DNA and were examined by confocal microscopy. PlkWT, YCplac111-GAL1-HA-EGFP-Plk; T210D, YCplac111-GAL1-HA-EGFP-PlkT210D; W414F, YCplac111-GAL1-HA-EGFP-PlkW414F; T210D/W414F, YCplac111-GAL1-HA-EGFP-PlkT210D/W414F; PlkΔC, YCplac111-GAL1-HA-EGFP-PlkΔC; Plk-N1–49, YCplac111-GAL1-HA-EGFP-Plk-N1–49; control, an irrelevant plasmid without EGFP. Plk-N1–49 contains only the N-terminal 49-aa residues of Plk fused to EGFP and serves as a background EGFP signal. DIC, differential interference contrast; Plk, EGFP–Plk expression; PI, propidium iodide staining of nuclei; Plk + PI, EGFP–Plk and propidium iodide images superimposed. (Bar = 5 μm.)