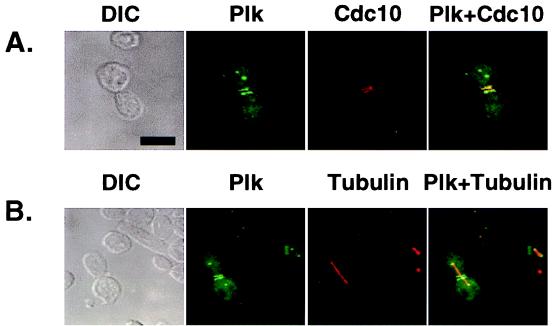
Figure 5.
Ectopically expressed Plk localizes at the spindle poles and bud neck filaments. EGFP–Plk fusion constructs were expressed under the control of the GAL1 promoter in a diploid wild-type strain, 1788. To enhance the signals present at the spindle poles and the cytokinetic septal structures, two tandem EGFPs were inserted into the N terminus of the Plk coding sequence. Transformants were cultured for subsequent immunostainings to examine Cdc10 and tubulin localizations. (A) Plk (green) and Cdc10 (red) localize at the neck filaments. Septin rings (red) are viewed edge on and therefore appear as lines. (B) Plk (green) localizes at the spindle poles. Spindles are visualized by microtubule staining (red). The spindles appear to emanate from the structures with which Plk associates. DIC, differential interference contrast; Plk, EGFP–Plk expression; Cdc10, Cdc10 staining; Tubulin, tubulin staining. Superimposed images are shown as Plk + Cdc10 and Plk + Tubulin. (Bar = 5 μm.)