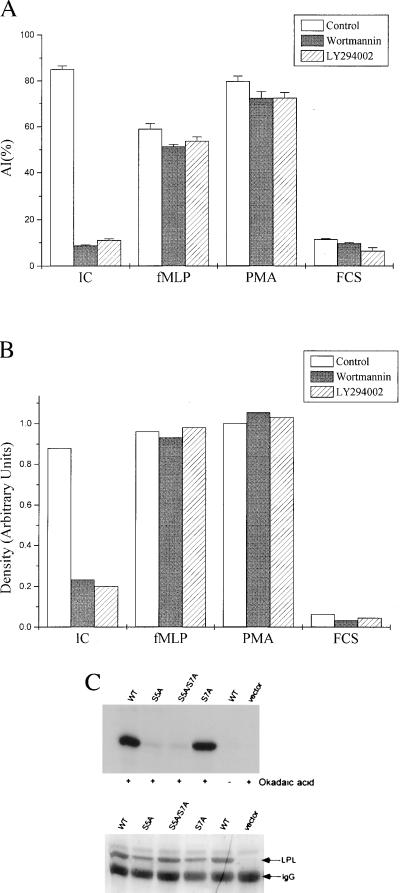
Figure 2.
The same proximal pathways that activate αMβ2-mediated adhesion induce phosphorylation of serine 5 of LPL. (A) PMN loaded with the fluorophore calcein were treated with control buffer, wortmannin (100 nM), or LY294002 (25 μM) before measurement of adhesion to IC (30 min) or fMLP- or PMA-induced adhesion to FCS (3 min). The data are the mean ± SE of triplicate wells, reported as attachment index (AI), which is the percentage of cells that remain adherent after washing. Wortmannin and LY294002 significantly inhibited adhesion to IC, but did not affect fMLP- or PMA-stimulated adhesion to FCS (<0.05). The data are representative of three separate experiments. (B) PMN loaded with [32P]phosphoric acid were treated with control DMSO, wortmannin (100 nM), or LY294002 (25 μM) and allowed to adhere to plates coated with IC or FCS or stimulated in suspension with fMLP (100 nM) or PMA (50 ng/ml) for 20 min at 37°C. LPL was immunoprecipitated and phosphorylation was quantitated by densitometry of autoradiograms. Data are normalized to maximal LPL phosphorylation induced by PMA. Each point represents the average of two separate experiments. (C) LPL or S5A, S7A, or S5A/S7A mutants of LPL were expressed in HeLa cells. After 6 hr of infection, the cells were loaded with [32P]phosphoric acid and treated with buffer control or the serine phosphatase inhibitor okadaic acid (1 μM) for 30 min at 37°C. LPL phosphorylation (C Upper) was assayed as in B. Loading of LPL was assessed by Coomassie blue stain (C Lower). Results are representative of three separate experiments.