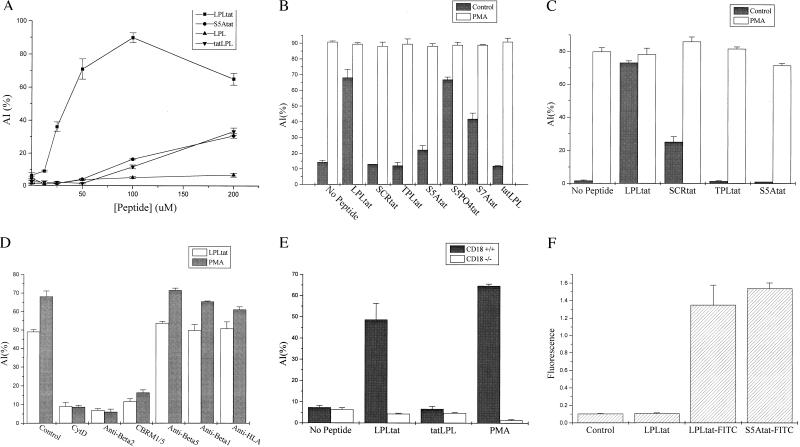
Figure 3.
Cell-permeant peptides from the amino terminus of LPL activate leukocyte integrin-mediated adhesion. To measure peptide effects on adhesion, purified PMN (A, B, D, and E) or monocytes (C) loaded with calcein were added to microtiter-plate wells coated with FCS followed by the addition of peptides with or without PMA (50 ng/ml) and incubated for 15 min at 37°C. (A) Peptide dose response. (B and C) One hundred micromoler of various peptides. The data are the mean ± SE of triplicate wells. Results are representative of at least three separate experiments. (D) Effects of cytochlasin D (10 μg/ml), anti-β2 F(ab′)2 mAb IB4, CBRM1/5, or the control anti-β1, anti-β5, or anti-HLA mAbs (all 20 μg/ml) on LPLtat-induced adhesion. (E) Adhesion of purified murine bone marrow PMN from wt (+/+) or CD18 (β2 integrin)-deficient (−/−) mice. (F) PMN were incubated with FITC-conjugated peptides and washed, and total fluorescence was quantitated by flow cytometry after quenching the extracellular fluorescence with the addition of 0.1% trypan blue dye. Data are presented as the mean ± SE fluorescence for three separate experiments.