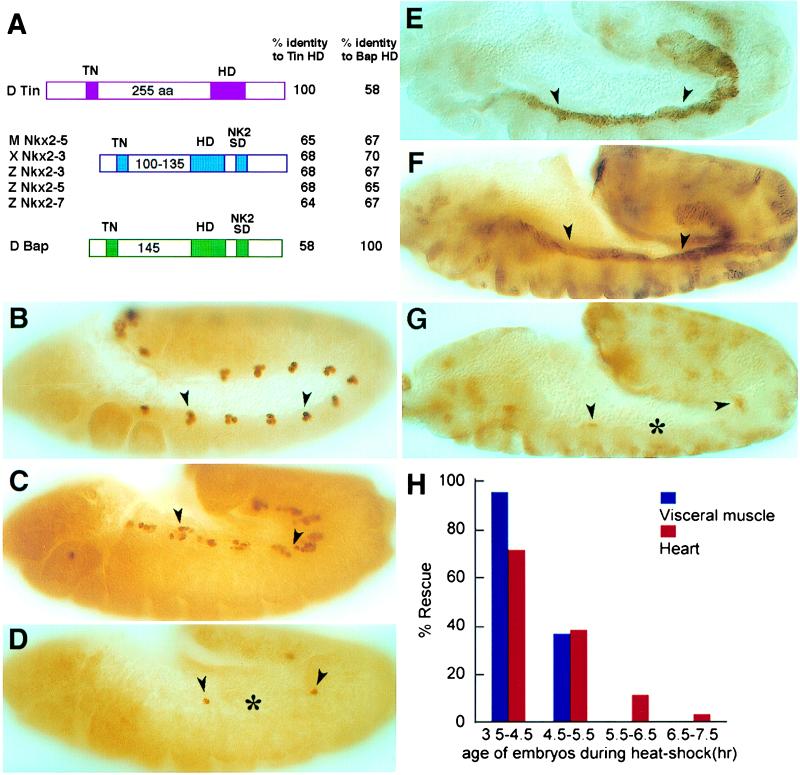
Figure 1.
(A) List of the cDNAs used in this study: Drosophila tin (D Tin), Nkx2–5 from mouse (M Nkx2–5/Csx) and zebrafish (Z Nkx2–5), Nkx2–3 from Xenopus (X Nkx2–3) and zebrafish (Z Nkx2–3), and Nkx2–7 from zebrafish (Z Nkx2–7). Approximate gene structures and sequence identities of the Nkx genes to tin and bap are indicated. TN, Tin/Nkx-specific domain of 11 amino acids (4, 8); HD, homeodomain; NK2-SD, NK2-specific domain (8). (B–G) Immunocytochemical staining. Eve expression (B–D) in a subset of cardiac progenitors along the dorsal mesodermal border (arrowheads) and FasIII expression (E–G) in the visceral mesoderm (arrowheads) of stage 12 wild-type embryos (B and E), homozygous Hstin,tinGC14 embryos (C, D, F, and G) heat shocked for 30 min between 3.5 and 4.5 hr of development (stage 9, C and F) or between 5 and 6 hr of development (early stage 11, D and G). Asterisks indicate the absence of marker gene expression in the presumptive heart (D) and visceral mesoderm (G) when heat shocked later. (H) Graph represents the amount of marker gene expression in presumptive cardiac (Eve expression in red) or visceral mesoderm (FasIII expression in blue) as a consequence of heat shock induction of the tin transgene. Each column represents the mean of 30 embryos or more. Anterior in all micrographs is to the left and dorsal is up.