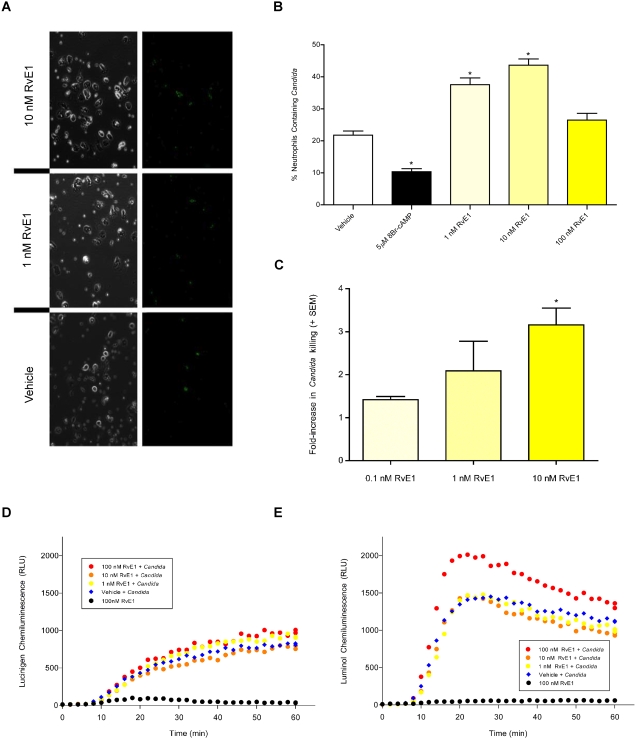
Figure 3. RvE1 enhances the effector functions of neutrophils.
(3AB) Neutrophil phagocytosis of FITC-stained heat-killed opsonized (HKO) C. albicans. (3B) Significantly more FITC-stained HKO C. albicans were phagocytosed by adherent human neutrophils treated with RvE1 (yellow bars) relative to vehicle-treated cells (open bar; asterisks indicate significant differences from vehicle-treated controls; ANOVA: p<0.001). Neutrophils treated with the non-hydrolyzable cAMP analog 8-bromo-cAMP were less likely to phagocytose the yeast (black bar). (3A) Representative images of isolated neutrophils phagocytosing FITC-stained HKO C. albicans in the presence of 10 nM RvE1, 1 nM RvE1 or vehicle and trypan blue. Green fluorescence (right panels) correspond to FITC-stained HKO C. albicans phagocytosed by neutrophils (3C) Neutrophils exposed to RvE1 exhibited a positive dose-dependent increase in their ability to kill opsonized C. albicans (yellow bars). Twice as many C. albicans were killed by neutrophils treated with 1nM RvE1 and over three times as many yeast were killed by neutrophils treated with 10 nM RvE1 relative to vehicle-treated neutrophils. Asterisks indicate significant differences from vehicle-treated controls (ANOVA: p<0.001). (3D) RvE1 had no effect on hydroxy-radical produced by neutrophils exposed to HKO C. albicans (red, orange, and yellow circles vs blue diamonds). (3E) 100 nM RvE1 increased neutrophil super-oxide production in neutrophils exposed to HKO C. albicans relative to neutrophils exposed to vehicle and HKO C. albicans (red circles vs blue diamonds) while lower concentrations of RvE1 (orange and yellow circles) did not increase neutrophil super-oxide relative to cells exposed to vehicle and HKO C. albicans (blue diamonds). 100nM RvE1 alone did not increase the amount of ROS produced by neutrophils relative to vehicle controls (3DE: black circles).