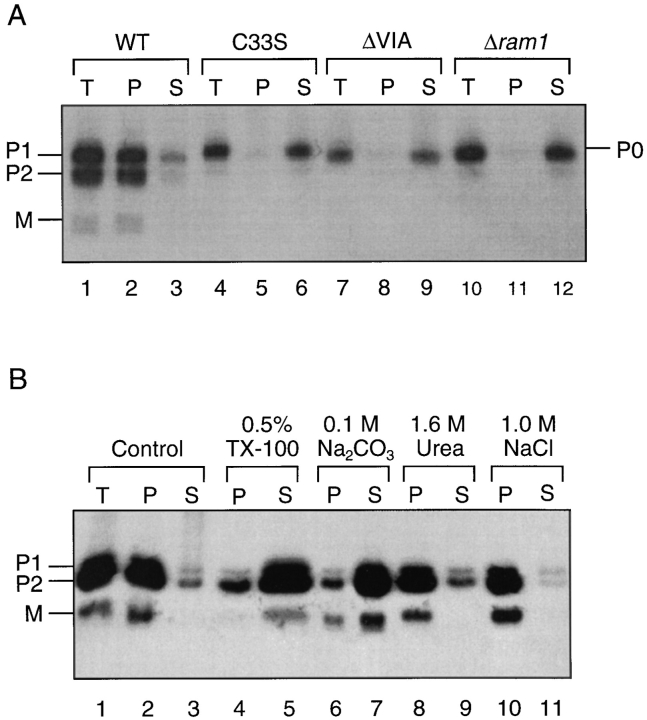
Figure 6.
Fractionation and solubilization properties of intracellular a-factor. In A, cells were labeled with [35S]cysteine for 5 min and lysates were prepared. The total cellular lysate (T) was separated into particulate (P) and soluble (S) fractions by centrifugation at 100,000 g for 1 h at 4°C. The a-factor species were immunoprecipitated and subjected to SDS-PAGE analysis. Strains examined in lanes 1–9 (SM1585, SM1682, and SM1680) carry either a wild-type or mutant MFA1 plasmid, as indicated. Strain SM1865, examined in lanes 10–12, is a Δram1 mutant. In B, a strain containing a wild-type MFA1 plasmid (SM1762) was labeled with [35S]cysteine for 5 min. The total lysate (T) was subjected to the indicated treatments or to no treatment (control, lanes 1–3) and subsequently separated into particulate (P) and soluble (S) fractions by centrifugation at 100,000 g for 1 h at 4°C. The a-factor intermediates were immunoprecipitated and analyzed by SDSPAGE and autoradiography.