Fig. (5).
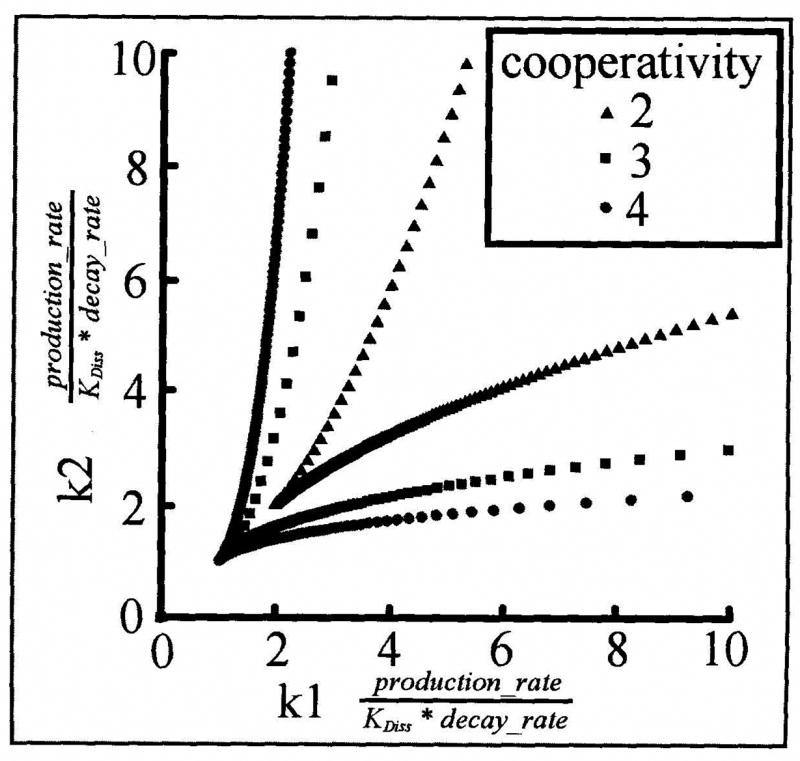
Parameter values for which a pair of mutually repressing genes will act as a mutual exclusion switch (adapted from [48]). So long as the repressive interactions of the two genes are greater than first order, a large range of parameter values (between the two dotted boundaries marked) results in robust switch-like behavior. The example boundaries shown are calculated assuming a Hill-function for the repressive interactions. In this case, the Hill coefficient stands in for cooperative binding on DNA and/or cooperative complex formation prior to DNA binding. Boundaries for Hill coefficients of 2, 3 and 4 are shown. The larger the degree of cooperativity, the more robust the mutual exclusion switch (larger area enclosed by the dotted boundaries).
