Figure 5.
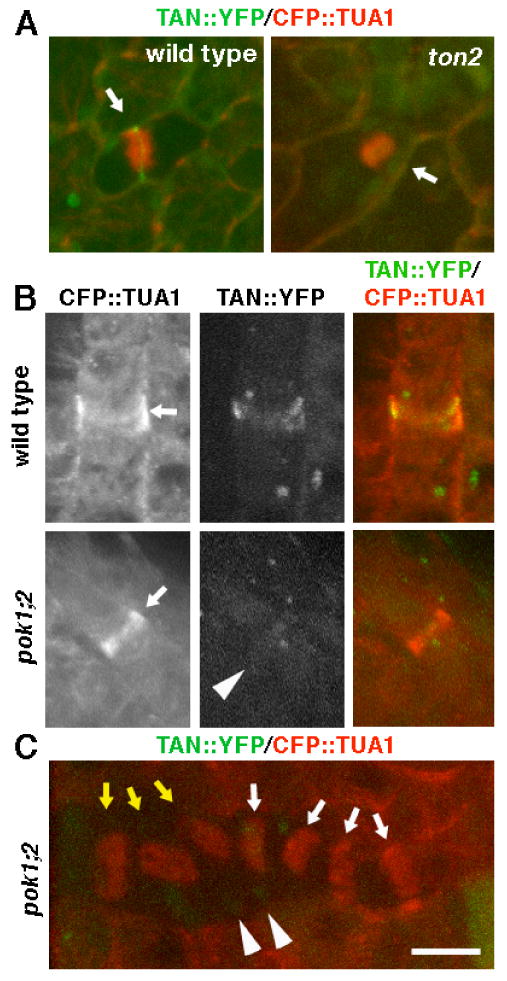
TON2 and POK1/POK2 are required for localization of AtTAN::YFP at the division site. A, Arrows point to cells with phragmoplasts in plants expressing AtTAN::YFP (green) and CFP::TUA1 (red) that are wild-type (left) or ton2 mutant (right). The wild-type cell has a well defined AtTAN::YFP ring and the ton2 mutant cell does not. B, Arrows point to a PPB in a wild-type plant (top) and a pok1;2 double mutant plant (bottom) expressing AtTAN::YFP (monochrome in second column, green in third column) and CFP::TUA1 (monochrome in first column, red in third column). The wild-type cell has a well-defined AtTAN::YFP ring, while the pok1;2 double mutant cell has only a very faint accumulation of AtTAN::YFP (arrowhead). C, pok1;2 double mutant cells with spindles (yellow arrows) and phragmoplasts (white arrows) labeled with CFP::TUA1 (red) lack well defined AtTAN::YFP rings (green). Arrowheads point to faint local accumulations of AtTAN::YFP (compare to wild-type AtTAN::YFP ring in A). Scale bar = 10μm.
