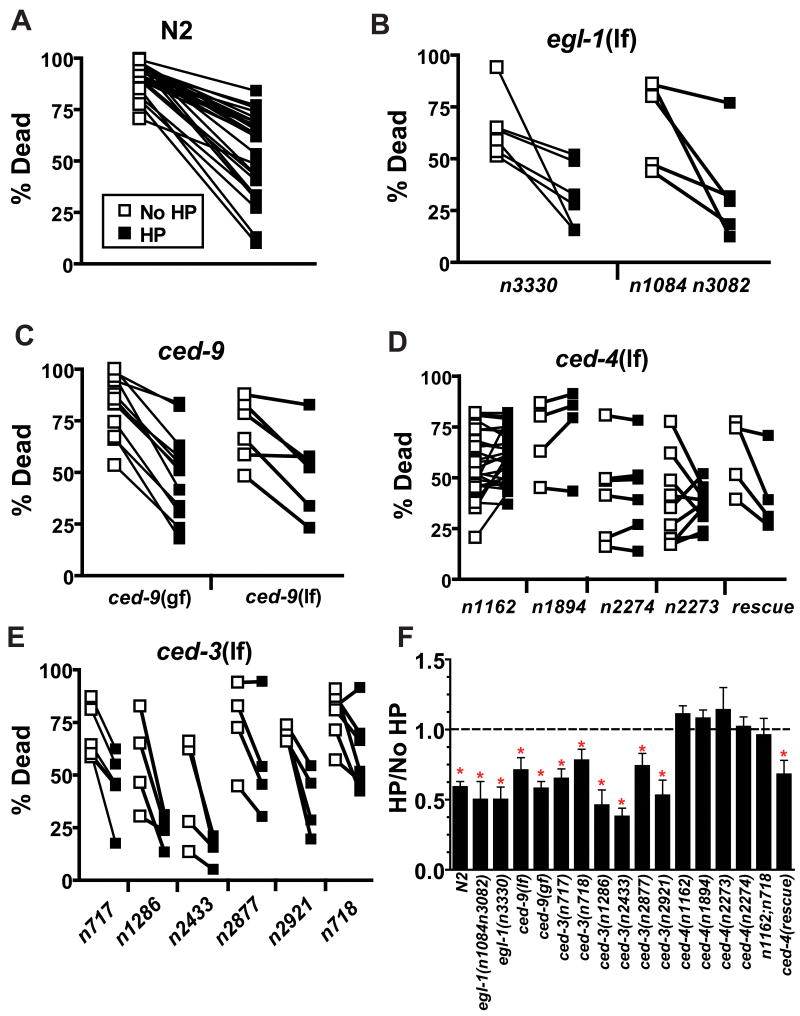
Figure 3. The Apaf-1 homolog CED-4 is required for HP.
(A–E) open symbols are data for no HP treated animals, closed symbols are for HP-treated animals. Data are paired by trial with concurrent HP and No HP animals. (A) Paired values for the wild type strain N2; the 26 paired trials that were done as controls for all of the programmed cell death pathway experiments are shown. (B) egl-1 is not required for HP. egl-1(n3330) and egl-1(n1084 n3082), both null alleles, are significantly protected by HP. (CB) ced-9 is not required for HP. Neither ced-9(n1950 gf) nor ced-9(lf) [full genotype - unc-69(e587) ced-9(n1950gf n2161lf); ced-3(n2433)] block HP. (D) ced-4 is required for HP. n1162, n1894, and n2274 carry stop codon mutations in the ced-4 gene and likely represent null alleles [18]. The rescue strain has the genotype ced-1(e1735);ced-4(n1162);unc-31(e928);nEx7[unc-31(+);ced-4(+)]. (E) Multiple ced-3 mutations do not block HP. (F) Summary of the effect of programmed cell death pathway mutants on HP. The ratio of the % dead in HP to that for No HP in each trial, mean ± sem; dotted line indicates unity. * - HP versus No HP significantly different by paired t-test, p < 0.05.