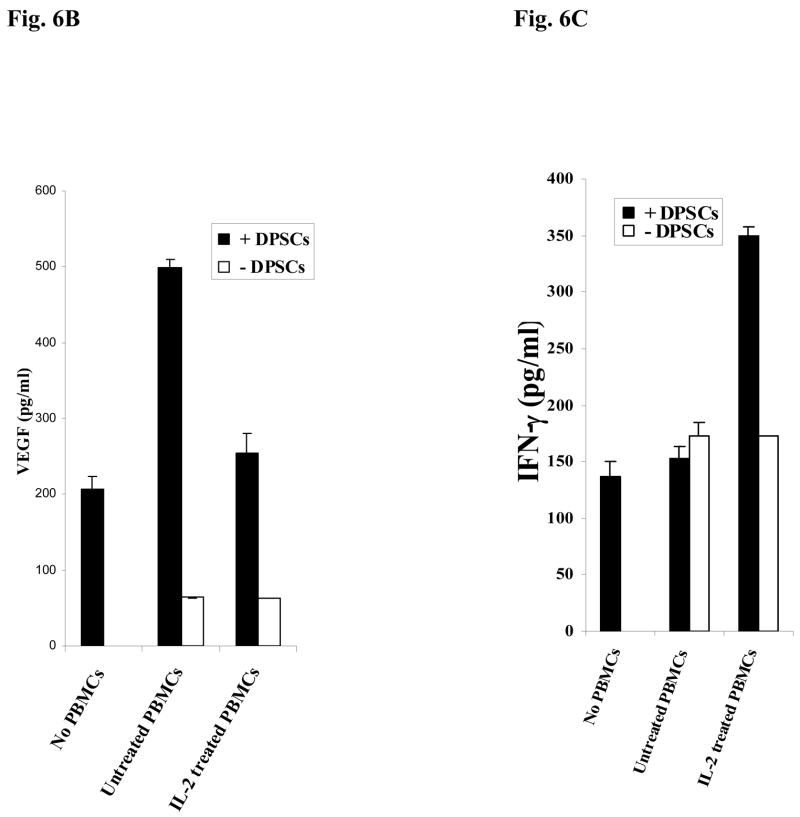
Fig-6. Increased Alkaline Phosphatase staining in DPSCs in the presence of naïve PBMCs and NAC.
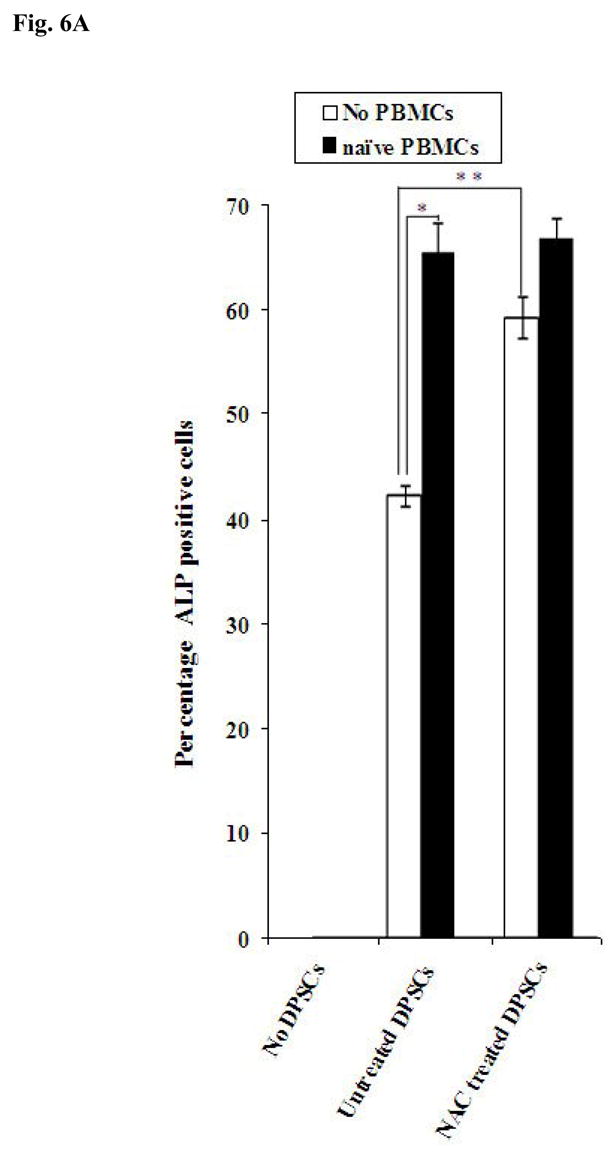
(A) Human DPSCs (2.5×105/ml) cultured with the combination of β-glycerophosphate (10 mM) and ascorbic acid (50μg/ml) were washed extensively and co-cultured with naïve non activated PBMCs (PBMC to DPSC ratio 10:1) for 3 days after which they were stained for Alkaline Phosphatase activity. The density levels of Alkaline Phosphatase staining for each well were determined using Adobe Photoshop software. One of three independent experiments is shown in this figure. (*p≤ 0.0001 and **p≤ 0.0001, unpaired, two-tail t-test) (B) Human DPSCs were treated as described in Fig. 6A and co-cultured with naïve and IL-2 (1000u/ml) treated immune cells (PBMC to DPSC ratio 10:1) for 18 hours and the supernatants were removed and assayed for VEGF secretion using a sensitive and specific ELISA. One of three independent experiments is shown in this figure. (*p≤ 0.001, unpaired, two-tail) (C) Human DPSCs were treated as described in Fig. 6A and co-cultured with naïve and IL-2 (1000u/ml) treated immune cells (PBMC to DPSC ratio 10:1) for 18 hours and the supernatants were removed and assayed for IFN-γ secretion using a sensitive and specific ELISA. One of three independent experiments is shown in this figure. (*p≤ 0.001, unpaired, two-tail)