Figure 4. Increased IL-1β release correlates with elevated apoptosis of IKKβ-deficient macrophages and is inhibited by PAI-2.
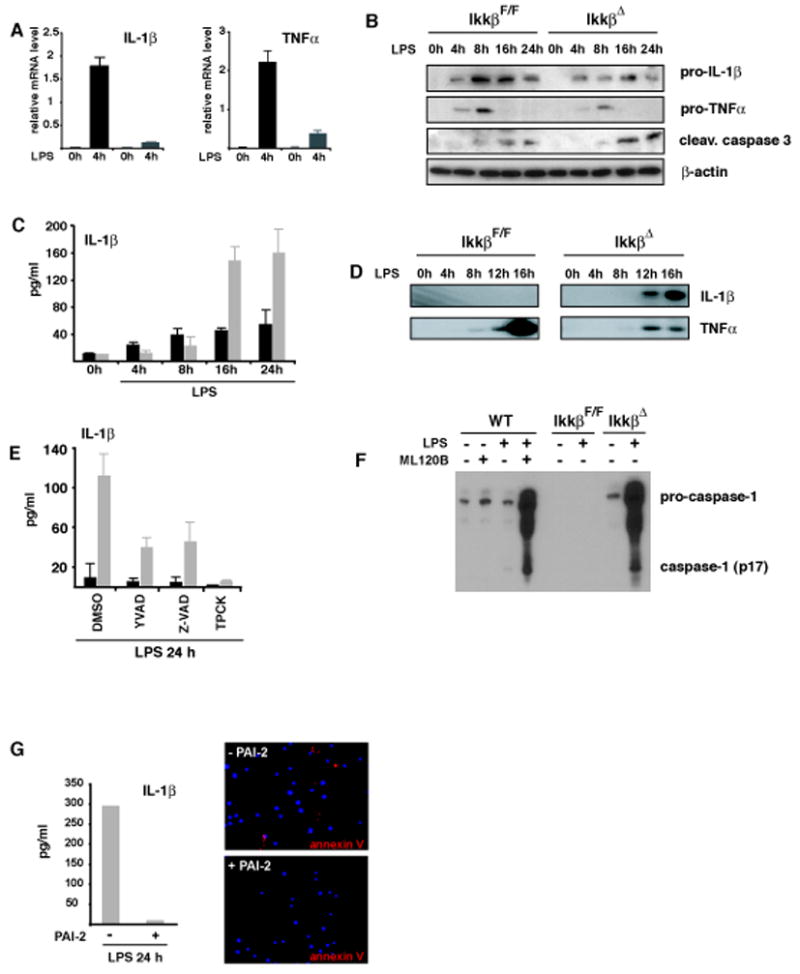
(A) Relative levels of IL-1β and TNF-α mRNA after incubation of IkkβF/F (black bars) and IkkβΔ (grey bars) BMDM with LPS (100 ng/ml). (B) Immunoblot analysis of intracellular pro-IL-1β, pro-TNF-α and cleaved caspase-3 in macrophages after LPS stimulation (100 ng/ml). (C) IL-1β levels in supernatants of IkkβF/F (black bars) and IkkβΔ (grey bars) macrophages after LPS stimulation. (D) Immunoblot analysis of processed IL-1β and TNF-α in supernatants of cultured macrophages. (E) IL-1β in supernatants of LPS stimulated IkkβF/F (black) and IkkβΔ (grey) macrophages in the presence of Ac-YVAD-cmk (100 μM), Z-VAD-fmk (10 μM) and TPCK (10 μM). Data are averages of at least three animals. (F) Loss of IKKβ activity enhances caspase-1 activation. WT or IKKβ-deficient macrophages were pretreated with ML120B (30 μM) or DMSO and either left unstimulated or incubated with LPS (100 ng/ml). After 22 hrs, culture supernatants were collected and analyzed by immunoblotting for secretion of activated caspase-1 (p17). The highest mobility represents uncleaved pro-caspase-1. (G) Reconstitution of IKKβ-deficient macrophages with PAI-2 blocks apoptosis and IL-1β release. Bone marrow of IkkβΔ mice was retrovirally transduced with EGFP-PAI-2. EGFP-positive cells were sorted, differentiated into macrophages and stimulated with LPS (100 ng/ml) for 24 hrs. Apoptosis was determined by annexin V staining and IL-1β levels in supernatants were determined by ELISA.
