Figure 6.
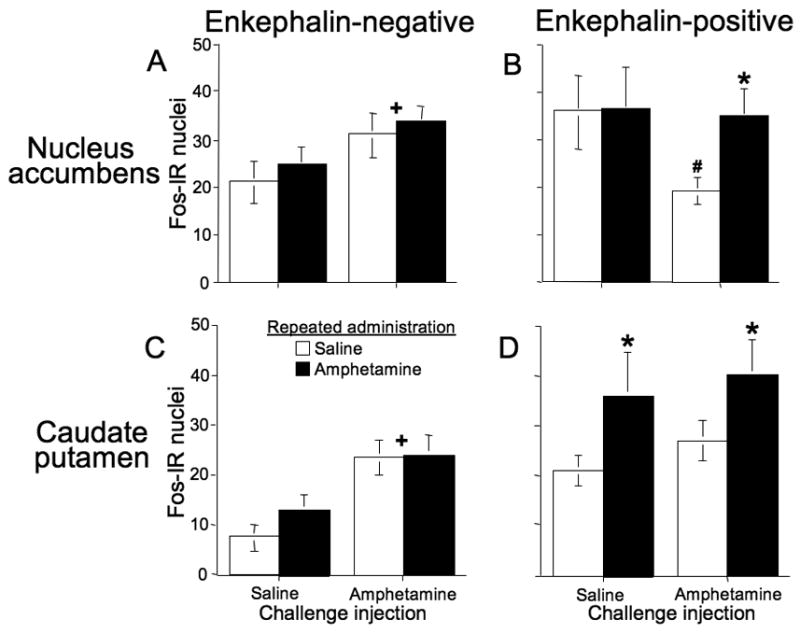
Levels of Fos expression in enkephalin-positive and enkephalin-negative neurons in the nucleus accumbens and caudate-putamen after repeated amphetamine administration in the locomotor activity chamber. For nucleus accumbens (A,B), asterisk indicates significantly more amphetamine-induced Fos-IR in enkephalin-positive neurons after repeated administration of amphetamine versus saline. Pound sign indicates that amphetamine challenge injections produced a significant decrease of Fos-IR in enkephalin-positive neurons after repeated saline administration. Cross sign indicates that amphetamine challenge injections significantly increased Fos-IR in enkephalin-negative neurons. For caudate-putamen (C,D), asterisks indicate significantly more Fos-IR after repeated administration of amphetamine versus saline. Cross signs indicate that amphetamine challenge injections significantly increased overall Fos-IR. Values represent mean±SEM (n=8 per group for amphetamine challenge injections; n=4 per group for saline challenge injections).
