Figure 2. Mechanism of MDSC induced T-cell tolerance.
Experimental design with adoptive transfer and immunization was as described in Fig 1.
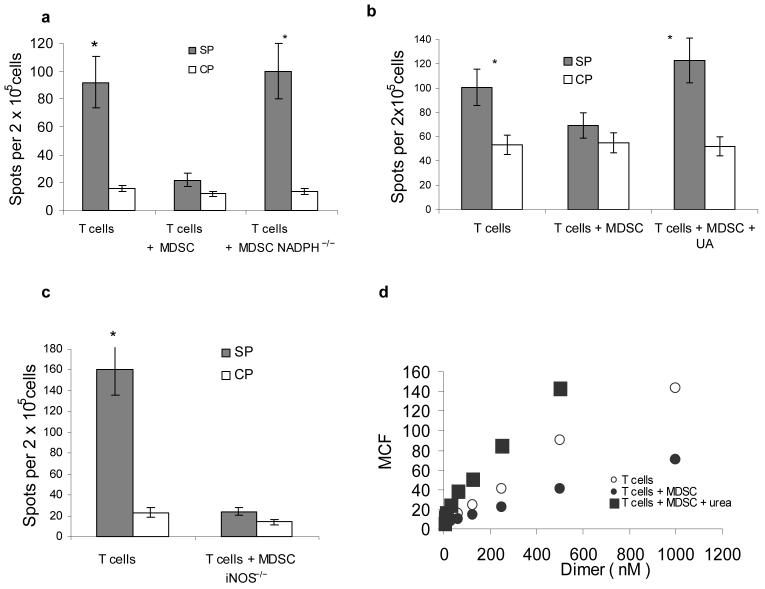
(a–c) IFN-γ ELISPOT assay of LN cells re-stimulated with control (CP) or specific (SP) peptides was performed. Results presented as Average ± SD per 2×105 LN cells. * - significant differences (p<0.05) between CP and SP groups. (a) MDSC from EL-4 tumor-bearing NADPH−/− (gp91phox−/−) or wild-type mice were used for adoptive transfer. Mean ± st. dev. from three performed experiments are shown (b) Mice were treated with UA in suspension (20 mg in 100 μl) on days -1, 0, 1, and 2 after MDSC transfer. (c) MDSC from EL-4 tumor-bearing iNOS−/− mice were used for adoptive transfer. Two experiments with the same results were performed.
(d) LN cells from OT-1 mice were cultured with 10 μg/ml SIINFEKL and MDSC (at 3:1 ratio) for 48 h in the presence of 1 mg/ml urea. After that time the binding of control and specific pMHC to CD8+ T cells was evaluated using flow cytometry as described in Fig. 1. T – T cells incubated without MDSC; T+MDSC- T cells incubated with MDSC; T + MDSC+Urea − T cells incubated with MDSC in the presence of urea.