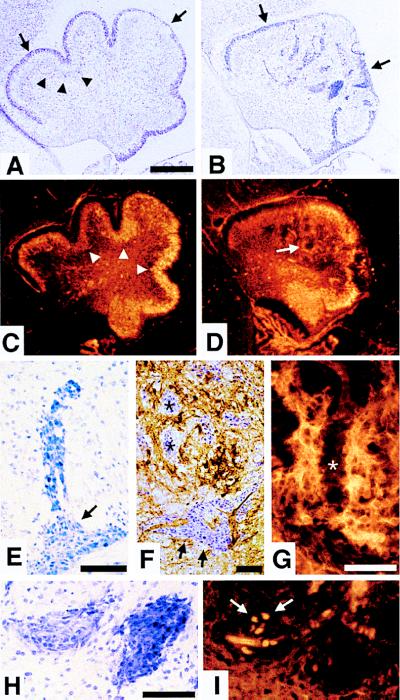
Figure 5.
Abnormal neuronal cell migration in CXCR4−/− cerebellum. Parasagittal sections of E18.5 cerebellum with anterior to the left and dorsal to the top. (A and B) Nissl staining. The EGL (arrows) of wild-type cerebellum (A) lies between the meninges and the diffuse Purkinje cell layer (partially marked by arrowheads). The abnormal cerebellum in CXCR4−/− mice (B) has an irregular EGL (arrows) and large chromophilic cell clumps within the cerebellar anlage. (C and D) Calbindin immunohistochemistry. In comparison with the Purkinje cell layer (arrowheads) in wild-type cerebellum (C), Purkinje cells are located ectopically (arrow) in CXCR4−/− cerebellum (D). (E–I) Chromophilic cell clumps in CXCR4−/− cerebellar anlage. Streaming cells from the EGL (E). Combined Nissl and calbindin staining (F). Purkinje cell neurites do not extend into the clumps (asterisks) (G). Adjacent sections stained by Nissl technique (H) or BrdUrd incorporation (I). Scale bar is 200 μm (A–D) and 50 μm (E–H).