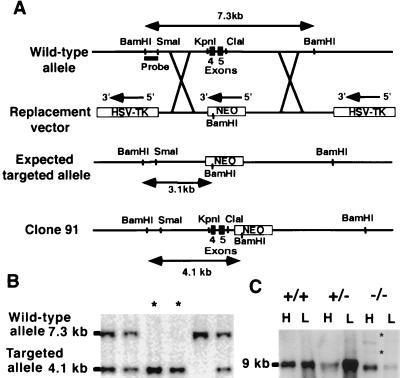
Figure 1.
Targeting of the vWf gene by homologous recombination. (A) The wild-type vWf locus is shown on the top. To make the replacement vector, a 800-bp KpnI–ClaI fragment including exons 4 and 5 of vWf was deleted and replaced with a 1.7-kb neomycin gene cassette driven by a PGK promoter. The 5′ flanking probe used for screening ES cell clones and genotyping mice by Southern blot analysis is indicated. The probe detects a 7.3-kb BamHI fragment in the wild-type allele and a 3.1-kb BamHI fragment in the expected targeted allele. The bottom line shows the targeted clone actually obtained with the retained KpnI–ClaI sites and the neo insertion in intron 5 of vWf. In this clone (clone 91), the probe recognizes a 4.1-kb BamHI fragment. (B) Southern blot analysis of genomic DNA isolated from tail biopsies of one litter resulting from heterozygous crossing. DNA was digested with BamHI, electrophoresed, and probed. Fragments recognized from wild-type and targeted alleles are indicated. Two mice are homozygous for the mutation (asterisks). (C) Northern blot analysis of vWf RNA: Total RNA was isolated from lung (L) and heart (H) of wild-type, heterozygous, and mutant mice. The vWf probe used was a 1-kb fragment from exon 28 of murine vWf cDNA. Several transcripts are present in the −/− mice. The bands indicated by asterisks also hybridized with a neo probe.