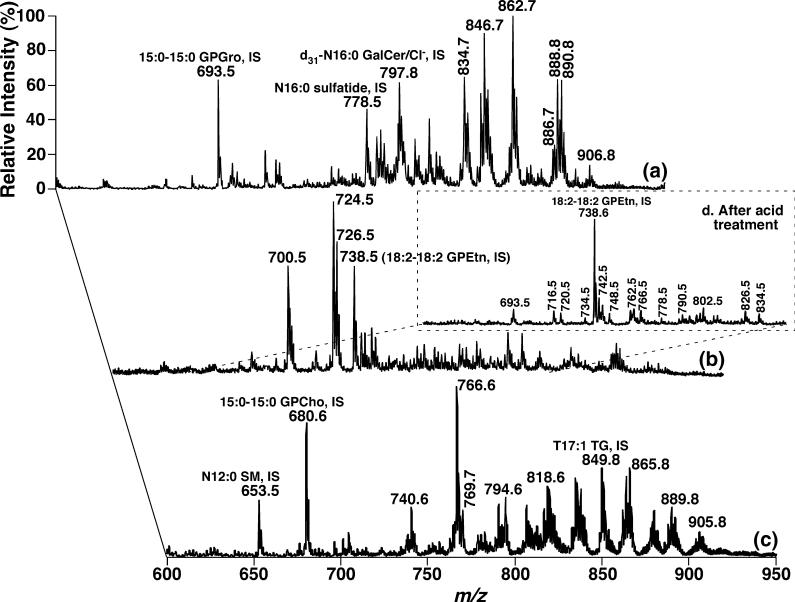
Fig. 1.
Electrospray ionization/mass spectrometry analyses of the mouse dorsal root ganglia lipidome after intrasource separation and selective ionization. Spectrum (a) was acquired in the negative-ion mode directly from a lipid extract that was diluted to less than 50 pmol of total lipids/μL. Spectrum (b) was acquired again in the negative-ion mode from the diluted lipid solution as used for spectrum (a) after addition of approximately 25 pmol LiOH/μL to the lipid solution. Spectrum (c) was acquired in the positive-ion mode from the identical diluted lipid solution as used in spectrum (b) after direct infusion. Spectrum (d) (inset) was taken in the negative-ion mode after the diluted lipid solution used in spectrum (a) was treated with acid vapor and a small amount of LiOH (approximately 25 pmol LiOH/μL) was added to the infused solution. The spectrum (d) is displayed after normalization of the ion peak of the glycerophosphoethanolamine (GPEtn) internal standard to that in spectrum (b). ‘IS’ denotes internal standard. All mass spectral traces are displayed after normalization to the base peak in each individual spectrum.