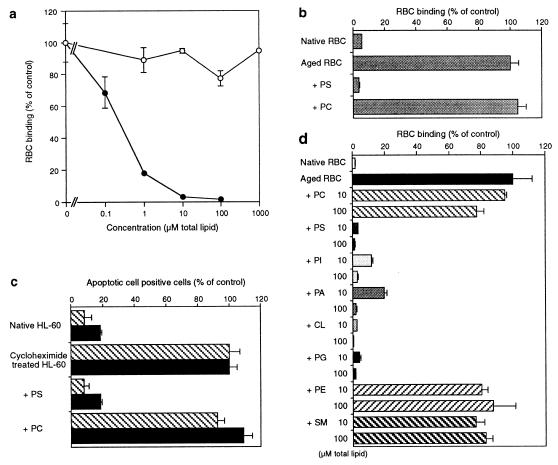
Figure 6.
Inhibitory effects of anionic phospholipid-liposomes on the binding of aged RBC and apoptotic HL-60 cells. (a) Binding of aged RBC to BLOX-1-CHO was inhibited by PS liposomes (•) dose-dependently, but not by PC liposomes (○). (b) Competition by PC and PS liposomes of the binding of aged RBC to BAE. The liposomes were used at 100 μM (total lipid). (c) Binding of apoptotic HL-60 cells to BLOX-1-CHO (cross-hatched bar) and BAE (solid bar) was inhibited by PS liposomes (100 μM total lipid), but not by the same amount of PC liposomes. (d) Inhibition by various phospholipid liposomes of the binding of aged RBC to BLOX-1-CHO. Binding of aged RBC was inhibited by anionic phospholipid liposomes, including PS, PI, phosphatidic acid (PA), cardiolipin (CL), and phosphatidylglycerol (PG), but not neutral phospholipid liposomes, PC, phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), and sphingomyeline (SM). Data represent the mean ± SEM of triplicate determinations. Values of 100% are the numbers of bound aged RBC or the numbers of BLOX-1-CHO associated with cycloheximide-treated HL-60 cells.