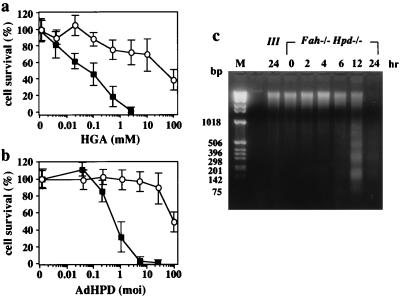
Figure 2.
Effect of HGA or exogenous expression of human HPD on cell viability in primary cultured hepatocytes derived from III and Fah−/− Hpd−/− mice. (a) The primary cultured hepatocytes were incubated in medium containing various concentrations of neutralized HGA. The viability of cells was calculated 24 h after exposure to HGA. ○, Means of survival for hepatocytes from III mice (n = 4); ■, those from the Fah−/− Hpd−/− mice (n = 6). The bars represents SD. Fah−/− Hpd−/− hepatocytes are significantly vulnerable to HGA, in a dose-dependent manner, compared with control III hepatocytes. (b) The primary cultured hepatocytes were transfected with recombinant adenovirus bearing human Hpd cDNA (AdHPD) to express HPD exogenously. The primary cultured hepatocytes were treated with various amounts of AdHPD, and the viable cells were calculated 24 h after infection by the recombinant virus. ○, means of survival for hepatocytes from III mice (n = 4); ■, those from the Fah−/− Hpd−/− mice (n = 6). The Fah−/− Hpd−/− hepatocytes are significantly and dose-dependently vulnerable to the infection by AdHPD, compared with control III hepatocytes. (c) Time-dependent progress of apoptotic death of primary cultured hepatocytes from Fah−/− Hpd−/− mice in the presence of 1 mM HGA. DNA samples were prepared from the cells after appropriate intervals and analyzed as described in the text. Lane M, DNA size markers. Fragmentation of genomic DNA from the hepatocytes of Fah−/− Hpd−/− mice was evident 6 h after the administration of HGA.