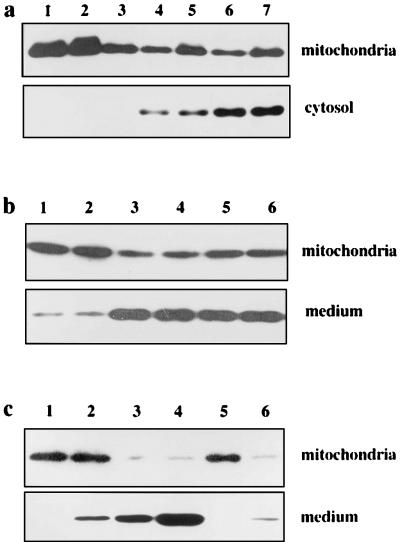
Figure 4.
Cytochrome c release from mitochondria in vivo and in vitro. (a) Immunoblot analysis of cytochrome c in the liver of Fah−/− Hpd−/− mice. Livers from variously treated mice were resected, and immediately mitochondrial and S-100 cytosolic fractions were prepared and subjected to SDS/PAGE and immunoblotting. Lane 1, untreated III mouse treated with HGA; lane 2, III mouse treated with HGA; lane 3, untreated Fah−/− Hpd−/− mouse; lane 4, Fah−/− Hpd−/− mouse 1 h after treatment with HGA; lane 5, Fah−/− Hpd−/− mouse 6 h after treatment with HGA; lane 6, DEVD-pretreated HGA-treated Fah−/− Hpd−/− mouse; lane 7, YVAD-pretreated HGA-treated Fah−/− Hpd−/− mouse. While a small amount of cytochrome c was detected in the cytosolic fraction (lanes 1–3), significant amounts of cytochrome c were detected in each lane in the case of cytosolic fractions of livers from Fah−/− Hpd−/− mice treated with HGA (lanes 4–7). The amounts of cytosolic cytochrome c remained unchanged by pretreatment with caspase inhibitors DEVD or YVAD (lanes 6 and 7). (b) Cytochrome c is released from control mitochondria in a cell-free system by the addition of cytosolic fraction from the HGA-treated Fah−/− Hpd−/− mouse. Mitochondria (1 mg) from control mice were incubated with S-100 fractions prefiltered to remove cytochrome c and other proteins, as described in the text. After incubation, the mitochondria and the supernatants were separated by centrifugation and analyzed for cytochrome c, using immunoblotting. Lane 1, III mouse treated with HGA; lane 2, untreated Fah−/− Hpd−/− mouse; lane 3, Fah−/− Hpd−/− mouse 1 h after treatment with HGA; lane 4, Fah−/− Hpd−/− mouse 6 h after treatment with HGA; lane 5, DEVD-pretreated HGA-treated Fah−/− Hpd−/− mouse; lane 6, YVAD-pretreated HGA-treated Fah−/− Hpd−/− mouse. A significant release of cytochrome c from mitochondria into the medium was evident in the fractions from HGA-treated Fah−/− Hpd−/− mice, whether pretreated with caspase inhibitors or not (lanes 3, 4, 5, and 6). (c) Cytochrome c is released from mitochondria by purified FAA. Mitochondria (1 mg) from the control mouse were incubated in the presence of purified FAA. After the incubation, the supernatant was analyzed for cytochrome c. Lane 1, buffer A only; lane 2, 1 μM FAA; lane 3, 10 μM FAA; lane 4, 100 μM FAA; lane 5, 10 μM HGA; lane 6, 100 μM HGA. Incubation of the purified FAA with control mitochondria resulted in release of cytochrome c into the medium.