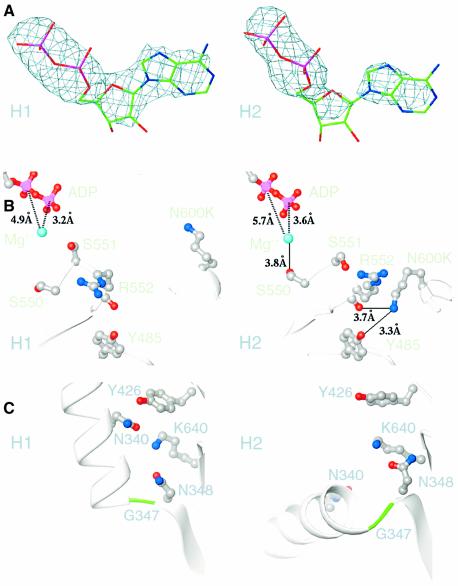
Fig. 2. Structural features of the two heads in the new structure. (A) Weighted Fo – Fc difference maps of the ADP bound to heads H1 and H2. The ADP bound to head H2 shows reduced density of the adenine base (right) and pentose ring (center) compared with the ADP of head H1, indicating that the adenosine is mobile or unstably bound. Map contoured at 3.5σ. (B) The mutated residue, N600K, of head H2 has moved toward R552 and forms a hydrogen bond (solid line) to R552 and Y485, causing S550 to hydrogen bond to the Mg2+ (cyan), destabilizing the bound ADP (ADP pyrophosphate, pink/red). This interaction is not observed in head H1. Distances, broken lines. (C) Movement of N600K towards R552 in head H2 weakens interactions between neck residue N340 and head H2 residues K640, N348 and Y426, permitting the coiled coil to rotate at G347 of head H2, while interactions of N340 with these residues in head H1 cause head H1 to rotate with the coiled coil.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.