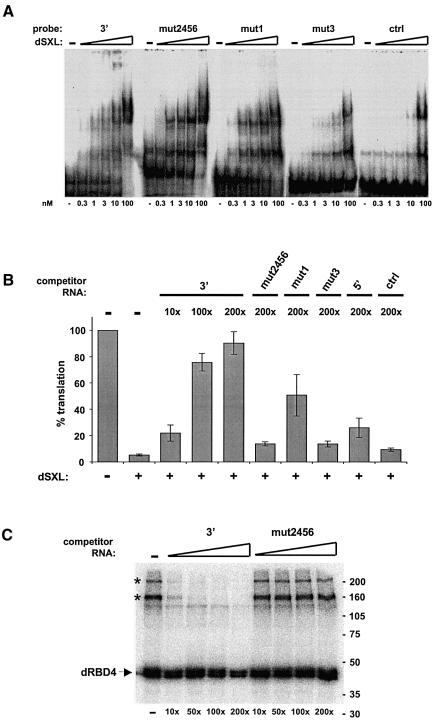
Fig. 7. Factors present in the Drosophila embryo extracts are required for translational repression of msl-2 mRNA. (A) Binding of dSXL to the 3′ probe or its derivatives (see Figure 6A), measured by gel mobility-shift assay. A probe containing the NRE of maternal hunchback mRNA was used as a specificity control (ctrl). (B) Functional titration of dSXL co-repressors. Drosophila embryo extracts were pre-incubated with 3′, mut2456, mut1, mut3, 5′ or control (multiple cloning site from pBluescript vector) RNAs, and typical translation reactions were subsequently assembled. The molar amount of competitor RNA was 10-, 100- or 200-fold higher than that of reporter mRNA. The translation assay was performed as described in Figure 1C. For simplicity, only the data obtained at 50-fold molar excess of dSXL over reporter mRNA are shown. Similar results were obtained with WT and BLEF mRNAs. (C) Specific titration of co-repressor crosslinking. Typical translation reactions containing Drosophila embryo extracts, 3′ probe and 50-fold molar excess of dRBD4 over probe were incubated with unlabelled 3′ or mut2456 competitor RNAs. The molar amount of competitor RNA was 10-, 50-, 100- or 200-fold higher than that of the probe. The UV-crosslink/co-immunoprecipitation assays were performed as described in Figure 4.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.