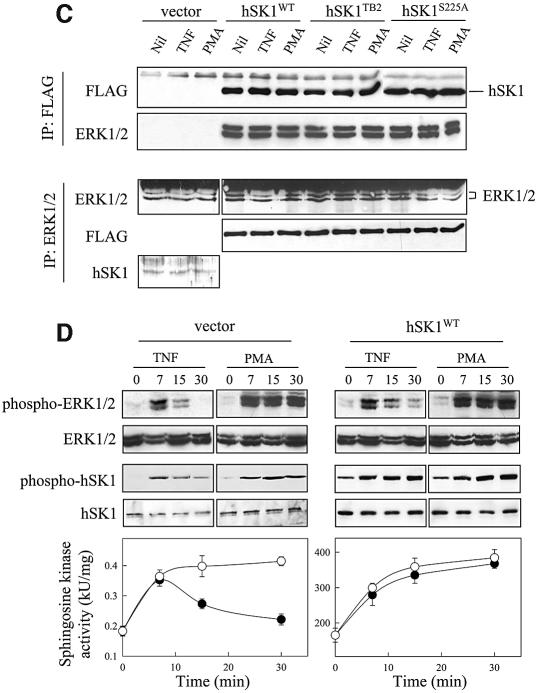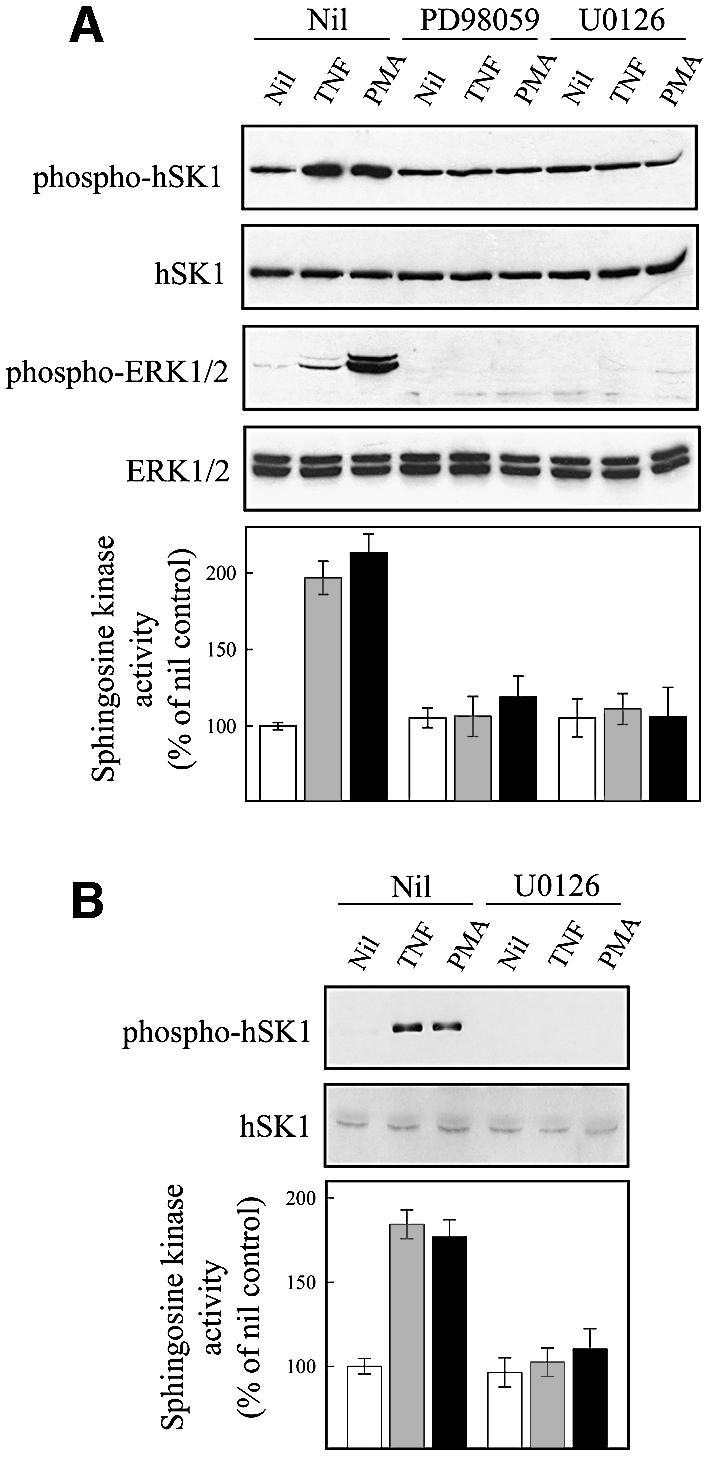
Fig. 5. ERK1 and -2 phosphorylate and activate hSK1 in vivo. (A and B) Agonist-induced phosphorylation and activation of hSK1 in HEK293T cells is blocked by ERK1/2 pathway inhibitors. Phosphorylation and activation of hSK1 in transiently transfected HEK293T cells (A) was followed by western blot using the phospho-hSK1 specific polyclonal antibodies (phospho-hSK1) and sphingosine kinase enzyme assays. HEK293T cells overexpressing wild-type hSK1 were treated with TNFα (1 ng/ml) or PMA (10 ng/ml) for 30 min in the presence or absence of the ERK1/2 pathway inhibitors PD98059 (10 µM) and U0126 (2 µM), added 30 min prior to TNFα or PMA. Total hSK1 levels were determined via the FLAG epitope, while ERK1/2 activation was followed by phospho-ERK1/2 and ERK1/2 antibodies. Phosphorylation of endogenous hSK1 in untransfected HEK293T cells showed similar results following treatment with TNFα (1 ng/ml for 10 min) and PMA (10 ng/ml for 30 min) in the presence or absence of U0126 (B). (C) Immunoprecipitation of ERK1/2 and hSK1. HEK293T cells overexpressing either wild-type hSK1 or hSK1TB2 were treated with TNFα or PMA for 30 min. hSK1 (via the FLAG epitope) or ERK1/2 from clarified cell lysates were immunoprecipitated, subjected to SDS–PAGE, and the protein complexes probed by western blot for ERK1/2, FLAG or directly for hSK1. (D) The time course of sphingosine kinase and ERK1/2 activation by TNFα (closed circles) and PMA (open circles) correlate in both empty vector and hSK1-transfected cells.