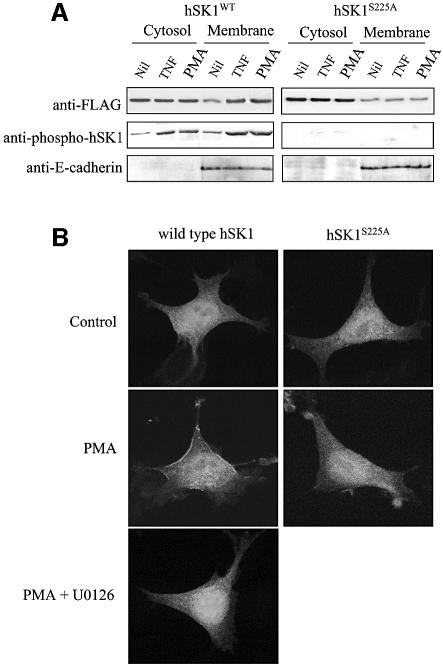
Fig. 6. Phosphorylation of hSK1 leads to its translocation to the plasma membrane. (A) Lysates from HEK293T cells transfected with wild-type hSK1 or hSK1S225A were fractionated into cytosol to membranes following treatment for 30 min with TNFα (1 ng/ml) and PMA (10 ng/ml). Cell fractions were then probed via western blot for total hSK1 (with anti-FLAG) and phospho-hSK1 to show phosphorylation-dependent translocation to the membrane fraction. Immunoblots for E-cadherin, an integral plasma membrane protein, were used to show equal membrane loading. Data are representative of three independent experiments. (B) Confocal microscopy of HEK293T cells transfected with either wild-type hSK1-GFP or hSK1S225A-GFP, with or without PMA (10 ng/ml), for 30 min showed phosphorylation-dependent translocation of hSK1 from the cytosol to the plasma membrane. This PMA-induced translocation of wild-type hSK1 was blocked by 30 min preincubation of the cells with U0126 (2 µM). Confocal images are representative of >50% of cells observed in three independent experiments.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.