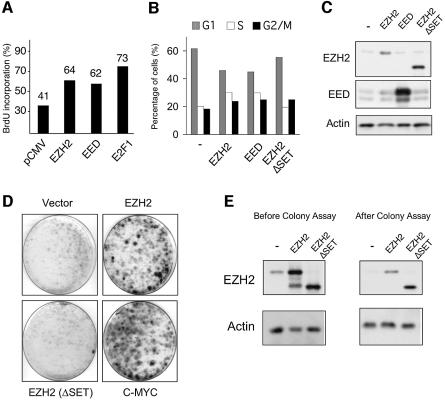
Fig. 4. Ectopic expression of EZH2 results in shorter G1 and prolongs the life span of primary MEFs. (A) Ectopic expression of EZH2 and EED increases the number of cells in S-phase. Serum-starved, quiescent Rat1 cells were injected with pCMV plasmids expressing either EZH2 or EED as indicated. Cells injected with E2F1 were used as a positive control. Serum was added to the serum-starved injected cells for 14 h prior to a 45 min pulse of BrdU. Relative DNA synthesis was determined by assessing BrdU incorporation by immunofluorescence. One representative experiment of five independent experiments is shown. (B) EZH2 ectopic expression results in S phase accumulation. Cell cycle phases of HeLa cells, transfected with the indicated plasmids, were determined 48 h after transfection by PI-FACS. (C) Western blot analysis of HeLa cells show similar expression of the wild type and mutant EZH2 proteins. (D) Expression of wild type EZH2, but not a SET-domain mutant, allows primary MEFs to form colonies, when plated at low density. Primary MEFs were infected with retroviral vectors expressing the indicated proteins. The experiment shown is representative of five independent experiments using different MEF preparations. (E) Western blot analysis of MEFs infected with the indicated retroviral vectors before and after the colony assay.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.