Figure 4.
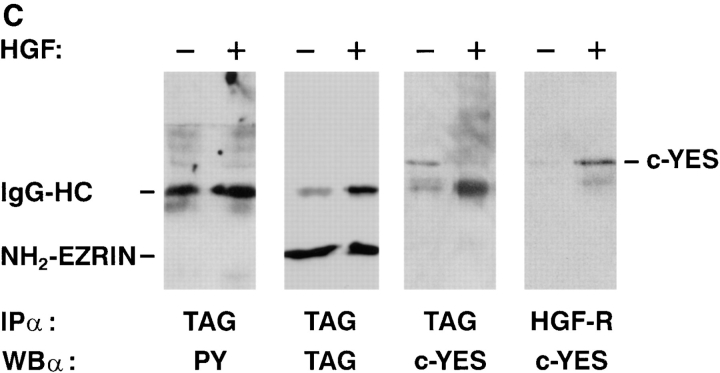
Wild-type ezrin is a substrate of the HGF-tyrosine kinase receptor. (A, left) In vitro kinase assay. GST-fused kinase domain of HGF-receptor (apparent molecular mass, 45 kD) was immobilized on glutathione–sepharose and incubated in the presence of 0.1 mM ATP alone (lane 1), with ezrin NH2-terminal domain (lane 2; apparent molecular mass, 38 kD), and with wild-type ezrin (lane 3; apparent molecular mass, 80 kD). Beads were washed, eluted in Laemmli buffer, and electrophoresed on 10% SDS-PAGE. Western blots were probed with rabbit anti–phosphotyrosine polyclonal antibodies. (Right) Western blot with anti–glutathione-S-transferase (GST) antibodies. 2 μg of GST proteins were loaded and detected with anti-GST polyclonal antibodies. (B) Tyrosine phosphorylation of ezrin and HGF-receptor and association of p62c-yes with ezrin and HGF receptor. E7 cells were unstimulated (−) and stimulated (+) in vivo with 120 ng/ml HGF, lysed, and immunocomplexes containing epitope-tagged ezrin and HGF-R were probed in Western blot with anti-phosphotyrosine antibodies (anti-PY; left two panels), and anti-p62c-yes polyclonal antibodies (right two panels). (C) Tyrosine phosphorylation of the NH2-terminal domain of ezrin, and association of p62c-yes with the ezrin NH2-terminal domain and HGF-R. N2 cells were unstimulated (−) and stimulated (+) in vivo with 120 ng/ml HGF, lysed, and immunocomplexes containing epitope-tagged NH2-terminal domain of ezrin were probed in Western blot with anti-phosphotyrosine, anti-tag, and anti-p62c-yes antibodies (left three panels). Immunocomplexes obtained with anti-HGF-R antibody were probed in Western blot with anti-p62c-yes antibodies (right).