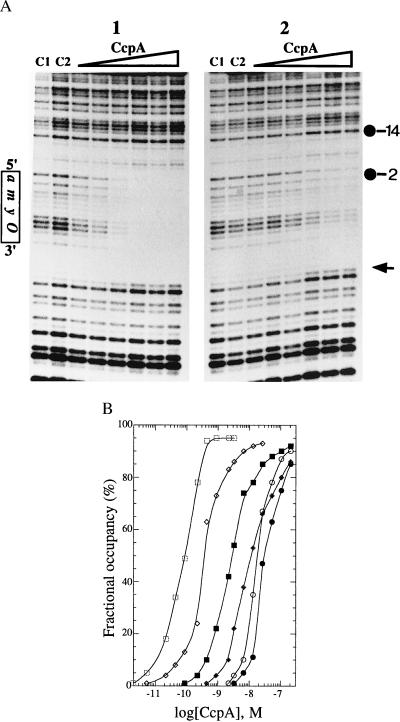
Figure 2.
Synergistic stimulation of combinations of HPr-P (Ser-46)/FDP and HPr-P (Ser-46)/NADP on CcpA binding to amyO. (A) DNase I footprints of amyO fragment bound by CcpA/HPr-P (Ser-46)/FDP (1) and CcpA/HPr-P (Ser-46)/NADP (2). After the various concentrations of CcpA (2.2 pM-2.2 nM) were incubated with HPr-P (Ser-46) (0.68 μM) and FDP (3 mM) or HPr-P (Ser-46) (0.68 μM) and NADP (1 mM), amyO fragments were added to the mixture to allow formation of amyO–CcpA complexes. The complexes were digested with DNase I. C1 and C2 represent the DNase I-digested amyO fragments without (C1) and with (C2) CcpA (28 nM), respectively. The DNase I hypersensitivity band is indicated by an arrow. (B) Titration of CcpA binding to amyO by CcpA alone (•) and CcpA combined with FDP (♦), NADP (○), HPr-P (Ser-46) (■), HPr-P (Ser-46) + FDP (□), or HPr-P (Ser-46) + NADP (⋄). The DNA-binding isotherms were derived from original footprinting gels such as those shown in A. Fractional occupancy (%) was obtained by quantifying and normalizing the band intensity of diagnostic band (−2G) to that of the reference band (−14A) and plotted as a function of CcpA concentration. Both bands are shown by numbers in the figure.