Abstract
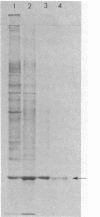
alpha-Pinene oxide is an intermediate in the degradation of alpha-pinene by Nocardia sp. strain P18.3 and some Pseudomonas strains. The epoxide is cleaved by a lyase which catalyzes a concerted reaction in which both rings of the bicyclic structure are cleaved with the formation of cis-2-methyl-5-isopropylhexa-2,5-dienal. The enzyme has been purified to homogeneity from Nocardia sp. strain P18.3. It was induced by growth with alpha-pinene and constituted 6 to 7% of the soluble protein of cell extracts. The apparent molecular weight of the native enzyme was 50,000 by ultracentrifugal analysis. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis gave two dissimilar subunits with apparent molecular weights of 17,000 and 22,000. The enzyme was devoid of prosthetic groups, had no cofactor requirement, and had a broad pH activity range, a Km for alpha-pinene oxide of 9 microM, and a turnover number of 15,000. Inhibitors included sulfhydryl reactive compounds, terpene epoxides, and pinane derivatives with substituent groups at carbon 3. A mechanism for the concerted reaction has been proposed in which decyclization is initiated by donation of a proton from the catalytic center to the oxygen of the epoxide with consequent destabilization. In vitro the enzyme was inactivated during catalysis, and a reactive cationic intermediate may be responsible for this phenomenon. The enzyme should be classified as a lyase EC 4.99.-.-.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Griffiths E. T., Bociek S. M., Harries P. C., Jeffcoat R., Sissons D. J., Trudgill P. W. Bacterial metabolism of alpha-pinene: pathway from alpha-pinene oxide to acyclic metabolites in Nocardia sp. strain P18.3. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):4972–4979. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.4972-4979.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YPHANTIS D. A. EQUILIBRIUM ULTRACENTRIFUGATION OF DILUTE SOLUTIONS. Biochemistry. 1964 Mar;3:297–317. doi: 10.1021/bi00891a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]