Figure 2.
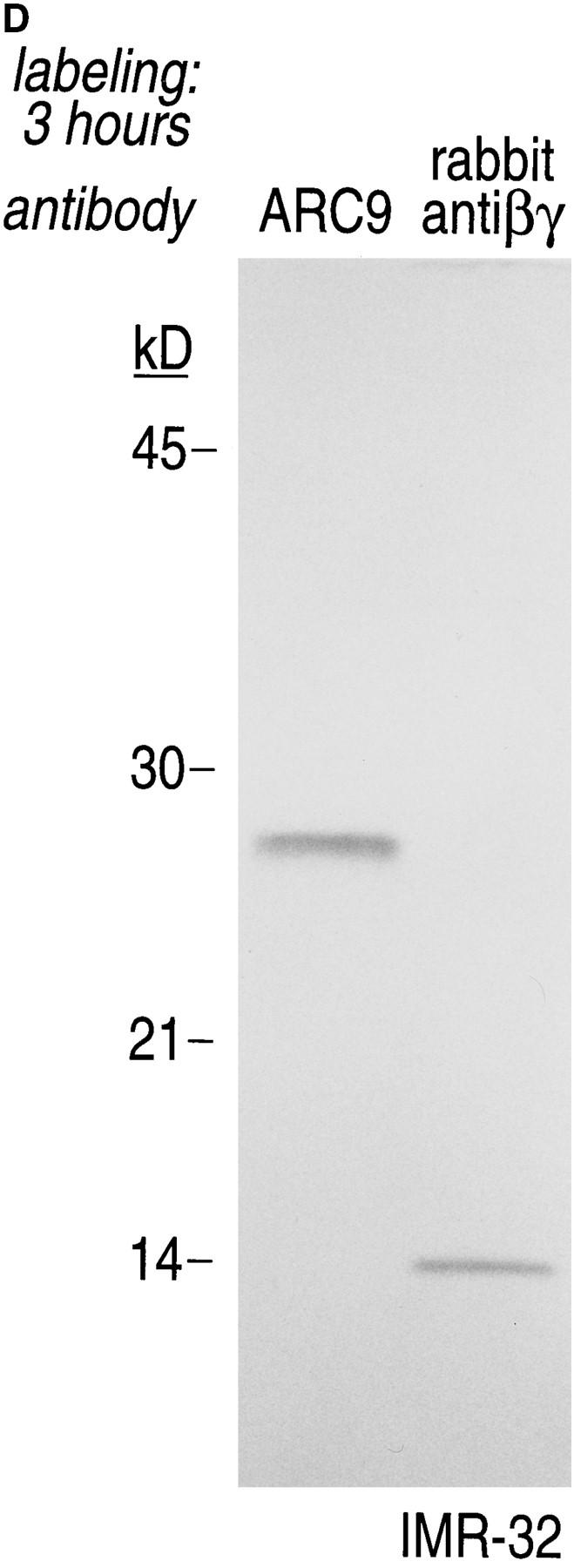
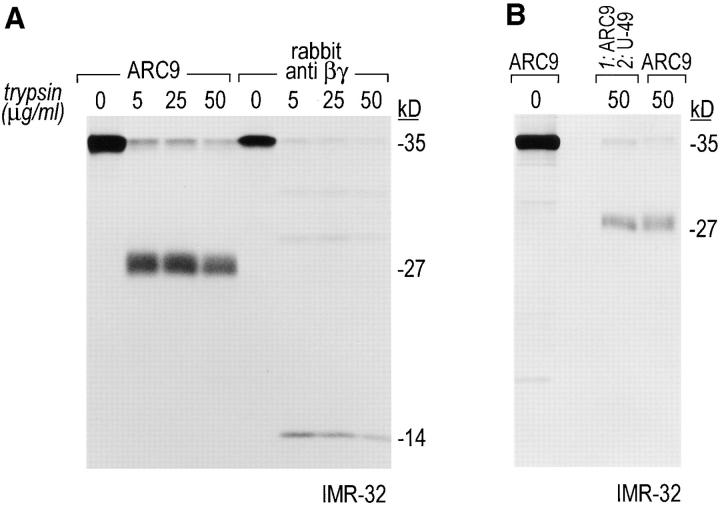
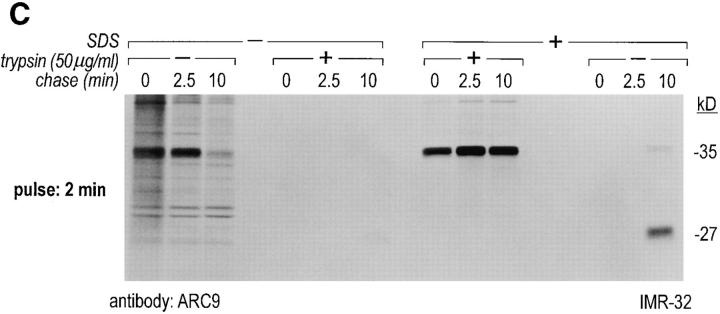
The generation of the βγ subunit derived 27-kD tryptic cleavage product in cell lysates is coincident with the appearance of newly assembled βγ complexes. (A) IMR-32 cells were labeled with 200 μCi [35S]methionine for 2 h. Cells were lysed in 0.3% Lubrol containing lysis buffer and trypsin was added at the concentrations indicated. Immunoprecipitations were done in the presence of 0.2% SDS using ARC9 or rabbit anti-βγ serum. The positions of undigested β chains and tryptic fragments are indicated on the right. (B) The origin of the 27-kD tryptic β fragment was confirmed by re-immunoprecipitation of ARC9 immunoprecipitates with the peptide-specific polyclonal antiserum U-49. (C) IMR-32 cells were pulsed for 2 min with 500 μCi [35S]methionine and chased for the times indicated. Lysates were prepared as in A, and trypsin was added at a concentration of 50 μg/ml. Immunoprecipitations were done in the presence and absence of 0.2% SDS. Note that the appearance of the 27-kD fragment is coincident with the loss of the (−) SDS form in untreated samples. (D) β and γ subunits are complexed in non-ionic detergent-resistant membrane domains. IMR-32 cells were labeled for 3 h with 150 μCi [35S]methionine and lysed in TX-100–containing lysis buffer. Detergent-resistant membranes were resolubilized in octyl-glucoside containing lysis buffer. Trypsin digestion was done as described before (A–C); immunoprecipitations with ARC9 and rabbit antiβγ serum resulted in the appearance of the 27-kD and 14-kD tryptic fragments.