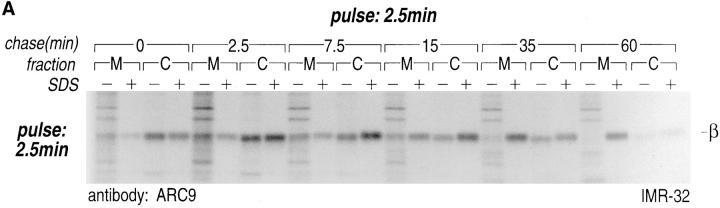
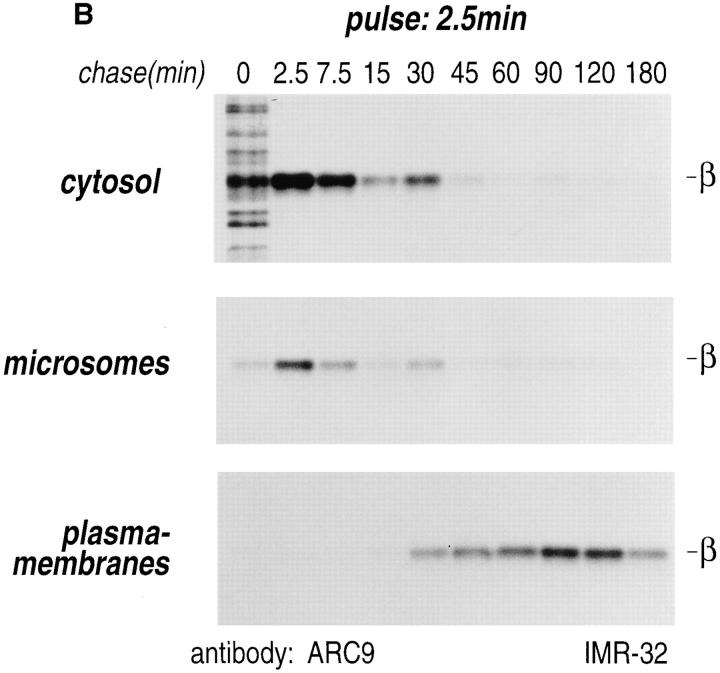
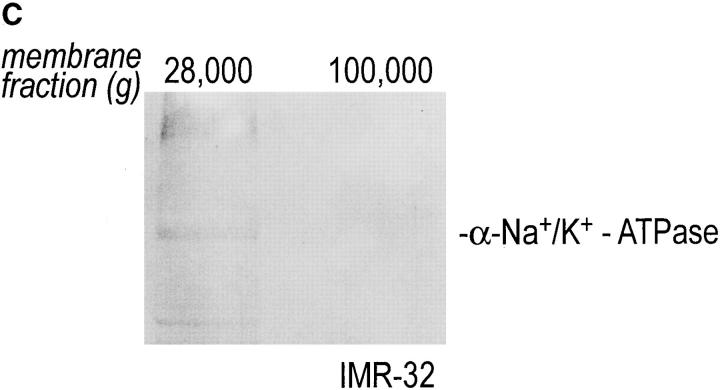
Figure 3.
Intracellular redistribution of newly synthesized Gβ subunits. (A) IMR-32 cells were pulse-labeled with 150 μCi [35S]methionine for 2.5 min and chased for the times indicated. A crude homogenate was separated into microsomes and cytosol by centrifugation at 100,000 g for 1 h at 4°C. The pellets recovered were considered the M fractions and contained plasma membranes and microsomal membranes, whereas the supernatant contained the cytosol (fraction C). Solubilization of subcellular fractions in NP-40/Lubrol lysis buffer was as for Fig. 1. Gβ was recovered in the absence (−) or presence (+) of 0.2% SDS. mAb ARC9 immunoprecipitates were analyzed on a 12.5% SDS-PAGE. (B) IMR-32 cells were pulse-labeled as in A and chased for up to 180 min. Membrane and cytosol fractions were prepared by differential centrifugation, yielding fractions designated plasma membranes (28,000 g pellet); microsomes (100,000 g pellet); and cytosol (100,000 g supernatant). All immunoprecipitations with ARC9 were done in the presence of 0.2% SDS. Samples were resolved by 12.5% SDS-PAGE. Although at 15-min chase some of the total cell lysate was inadvertently lost in this experiment, the ratio between the cytosolic and microsomal β as the relevant parameter can still be evaluated. (C) The plasma membrane marker α-Na+/K+-ATPase is detectable in the 28,000 g membrane fraction, but not in the 100,000 g pellet. 50-μg aliquots of membrane fractions as obtained in B were subjected to electrophoresis on a 12.5% SDS-PAGE and transferred to nitrocellulose. The blotting membrane was incubated with rabbit anti–α-Na+/K+-ATPase antiserum.