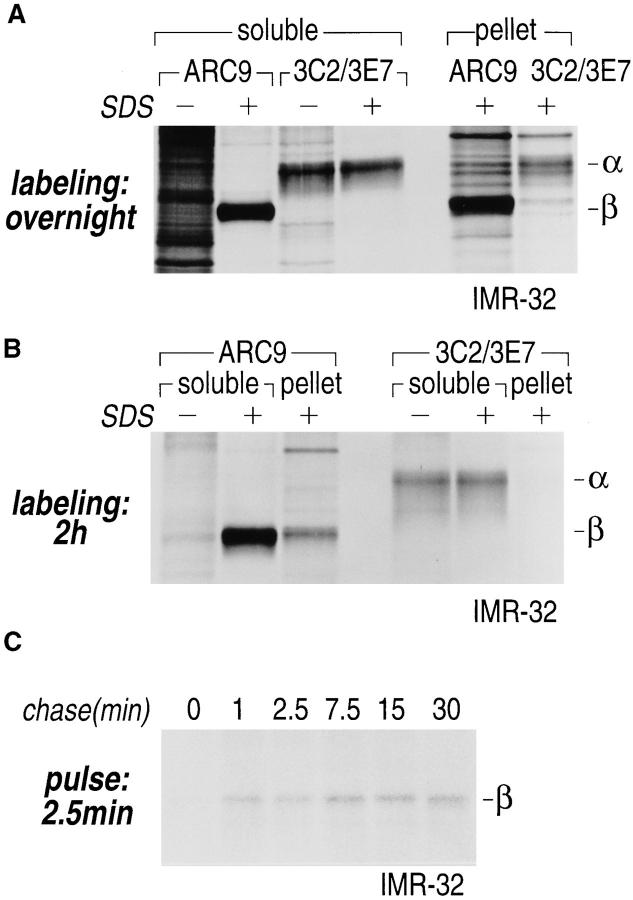
Figure 5.
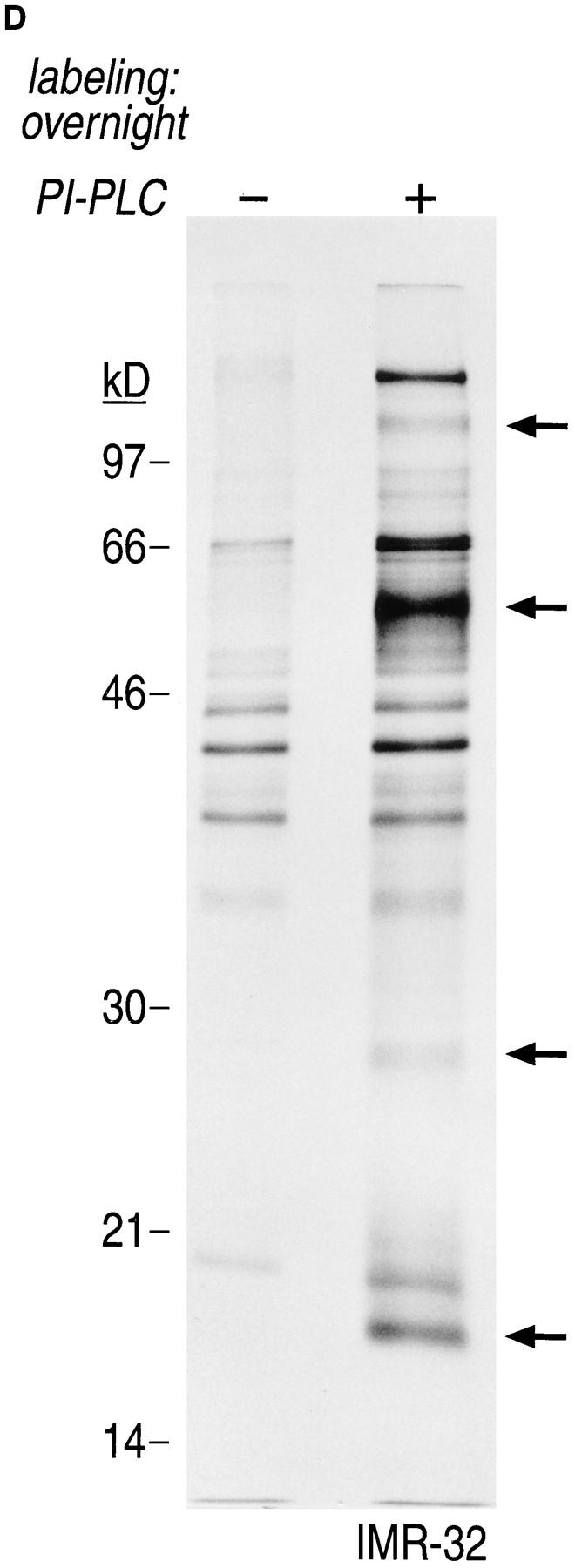
Gα and Gβ are associated with non-ionic detergent-insoluble cell pellets. (A) IMR-32 cells were labeled overnight with 100 μCi of [35S]methionine. Cells were lysed in NP-40/Lubrol lysis buffer and separated into supernatant (soluble) and insoluble pellet. The pellet was solubilized in 1% SDS, DNA was sheared by 15 passages through a 21-gauge needle and the extract was boiled twice at 100°C for 3 min. The SDS concentration in the pellet fraction was adjusted to 0.2% with NP-40/Lubrol lysis buffer. Immunoprecipitations from the supernatant were done either in the presence (+) or absence (−) of 0.2% SDS. A mixture of 3C2 and 3E7 were used to recover α subunits and β was precipitated with ARC9. Samples were analyzed on a 12.5% SDS-PAGE (A–C). Arrows indicate the positions of β and α subunits. (B) IMR-32 cells were labeled for 2 h with 250 μCi [35S]methionine followed by solubilization in NP-40/ Lubrol lysis buffer. Insoluble pellets were extracted twice with non-ionic detergent buffer and subsequently treated as shown in A. (C) Kinetics of Gβ subunit association with detergent-insoluble cell pellets. IMR-32 cells were pulsed for 2.5 min with 150 μCi [35S]methionine and chased for the time intervals indicated. Cells were separated into supernatant (soluble) and a detergent-insoluble pellet. The pellet was re-extracted as in A, followed by immunoprecipitation with ARC 9. (D) Detection of endogenous GPI-anchored proteins in non-ionic detergent-resistant membrane domains. IMR-32 cells were labeled overnight with 100 μCi [35S]methionine and lysed in buffer containing TX-100. After centrifugation, the resulting pellet was re-extracted with TX-114–containing lysis buffer for 20 min at 37°C. After centrifugation, the supernatant was subjected to temperature-induced phase separation. Samples were treated in the absence (−) and presence (+) of 5 U/ml PI-PLC. This treatment induces the transition from a hydrophobic to a hydrophilic state of GPI-anchored proteins. Polypeptides released into the aqueous phase were recovered by acetone precipitation and analyzed on a 12.5% SDS-PAGE. Arrows on the right indicate the appearance of some of the proteins specifically released by PI-PLC.