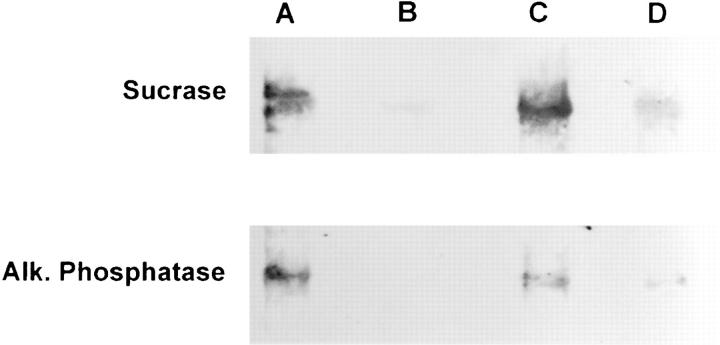
Figure 11.
Effect of A19 oligonucleotide on the polarity of sucrase isomaltase and alkaline phosphatase in CACO-2 cells. Confluent monolayers were grown on polycarbonate filters in the presence of random (lanes A and B) or A19 (lanes C and D) oligonucleotides as described above. The cells were biotinylated from the apical (lanes A and C) or basolateral sides (lanes B and D) and consecutively extracted in Triton X-114 at 4°C and with Triton X-100 at 37°C. The Triton X-114 detergent phase and the Triton X-100 supernatant were pooled and affinity purified with streptavidin–agarose. The eluates or the affinity purification step were then analyzed by immunoblot with antibodies against either sucrase isomaltase or alkaline phosphatase and a chemiluminescence detection system. The average OD measures obtained from unfiltered digitized images after subracting background from the average pixel value over the band of each lane were as follows (scale 0-255): (Sucrase A) 58; (B) 14; (C) 55; (D) 29; (Alk. Phosphatase, A) 74; (B) 1; (C) 30; (D) 16. Weighted OD measures (average pixel value × number of pixels) were as follows (in thousands): (Sucrase, A) 141; (B) 10; (C) 169; (D) 35; (Alk. Phosphatase, A) 45; (B) 0.6; (C) 36; (D) 5.