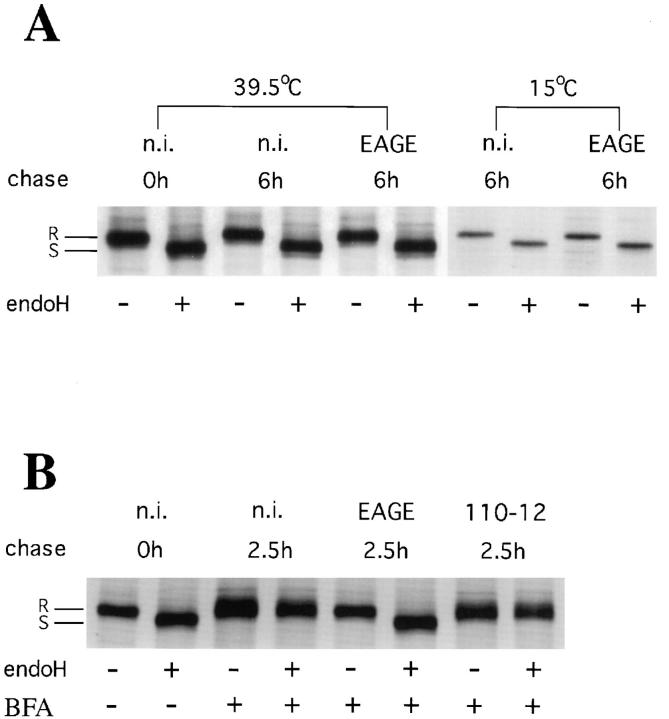
Figure 1.
Biochemical analysis of transfer of Golgi enzymes to the ER. Transfer of Golgi enzymes to the ER was determined biochemically by analyzing acquisition of endo H resistance of tsO45-G arrested in the ER. 500–1000 Vero cells infected with tsO45-VSV were incubated for 1.5 h at 39.5°C, metabolically labeled for 10 min with 35S-met and microinjected at 39.5°C or 15°C with Fab-fragments of anti-EAGE (EAGE), divalent anti–110-12 (110-12), or kept as noninjected controls (n.i.). (A) Noninjected control cells were lysed directly after the pulse with 35S-met and ts-O45-G analyzed for endo H sensitivity (0 h). 39.5°C: control or injected cells were lysed and ts-O45-G analyzed for endo H sensitivity after a chase of 6 h at 39.5°C; 15°C: temperature was shifted for 2 h to 15°C before injection at 15°C, and the cells were kept for an additional 4 h at 15°C before lysis and analysis of endo H resistance of ts-O45-G. (B) Control and injected cells were chased for 0 h or 2.5 h at 39.5°C in the presence of 5 μg/ml BFA before lysis and analysis of endo H resistance of ts-O45-G. Microinjected anti-EAGE, but not anti-110-12 block BFA induced acquisition of endo H resistance of ts-O45-G.