Figure 7.
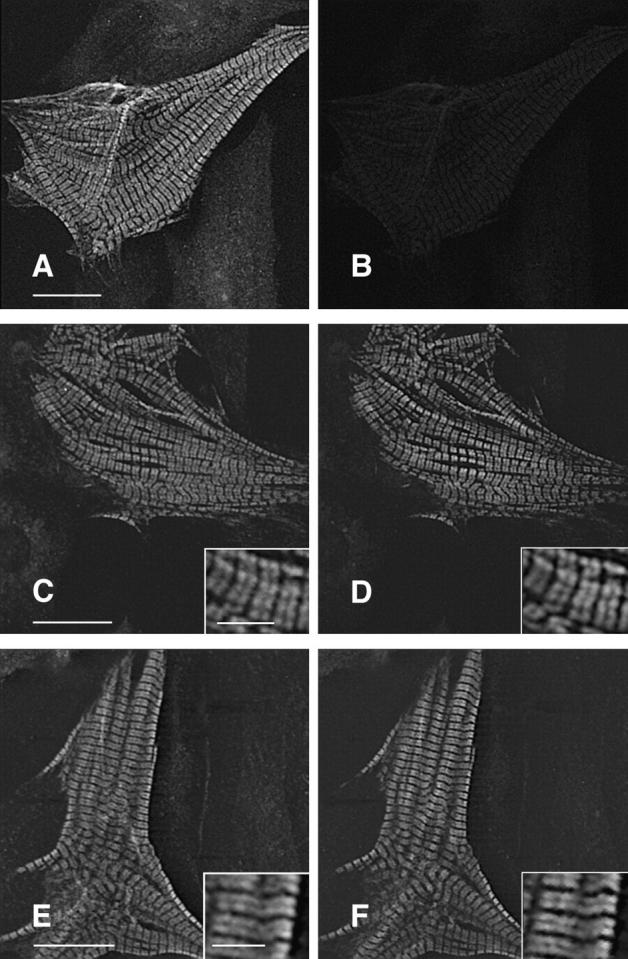
Coexpression of both mutant and wild-type βMHC molecules detects no differences in subcellular localization of the two exogenous proteins. NRC were cotransfected with both wildtype and mutant expression plasmids, each tagged with a different epitope. Sequential staining (see Materials and Methods) allows detection of each protein within the same cell. A and B show a cardiomyocyte transfected with Hnwt only. This cell was immunostained with anti-HA, goat anti–mouse–FITC (F(ab)), and anti- EE and then donkey anti–mouse–LRSC. A shows the anti-HA specific staining (FITC channel), and B shows the LRSC channel, indicating that the anti-EE antibody does not crossreact, and minimal signal bleed through occurs under these conditions. Using anti-EE to detect Tnwt, the same lack of crossreactivity is observed when costaining with anti-HA (data not shown). Expression and detection of both Hnwt (C) and Tnwt (D) in the same cell shows identical subcellular localization for both proteins. The TnR403Q mutant (F) also shows identical distribution to Hnwt βMHC (E) when coexpressed in the same cell. Similar results are obtained when coexpressing either R249Q or S472V with wildtype βMHC. The type of epitope does not affect the outcome of this experiment. Bars: (A, C, and E) 20 μm; (E and inset) 5 μm.
