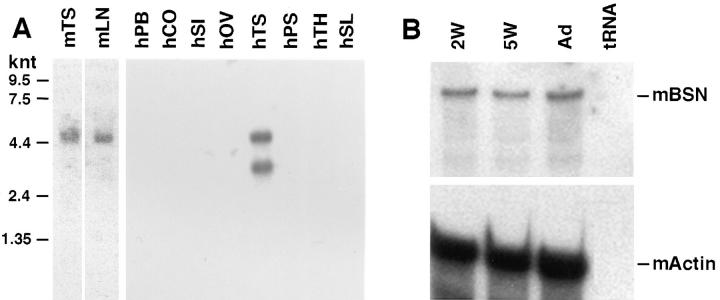
Figure 4.
Northern blot and RNase protection analyses. Northern blots of mouse and human RNAs were purchased from Clontech. Blots contained 2 μg polyA+ mRNAs, which were hybridized with a radiolabeled probe corresponding to a 576-bp fragment shared by BSN1a and BSN1b. As control, a radiolabeled probe corresponding to a 1-kb fragment of glyceraldehyde dehydrogenase was used. Note the presence of a 4,600-nucleotide band, predicted for the bona fide BSN1a and BSN1b RNAs, in testes samples (TS) from both mouse (m) and human (h); note the presence of an additional 3,200-nucleotide band in human testis. PB, peripheral blood; CO, colon; SI, small intestine; OV, ovary; TS, testis; PS, prostate; TH, thymus; SL, spleen. (B) RNAs were isolated from the testes of mice at 2 wk, 5 wk, and adult postnatally. RNAs were hybridized with radiolabeled mouse cRNas generated to either (a) a 576-nucleotide sequence common to BSN1a and BSN1b or (b) a 359-nucleotide actin sequence. After hybridization, RNase treatment was performed as described by Faus et al. (1994). Duplexes were resolved by PAGE, and the gel was exposed to x-ray film overnight. Note the presence of 487- and 250-nucleotide bands expected for BSN1a/BSN1b and actin RNAs, respectively, after hybridization with the probes and RNase digestion.