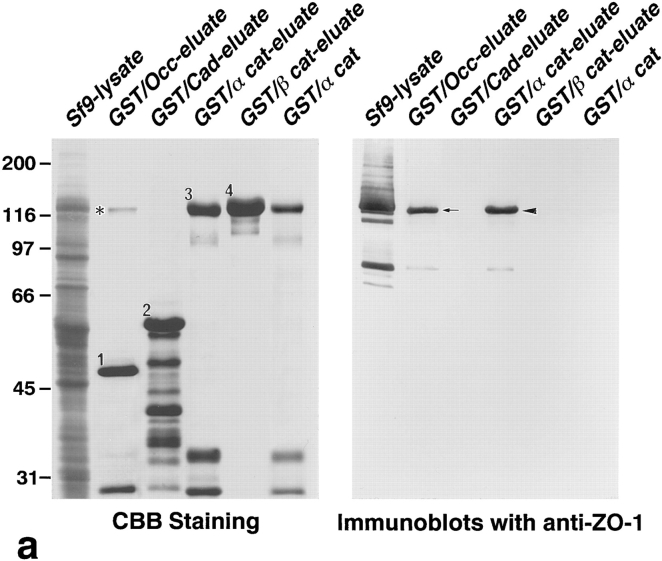
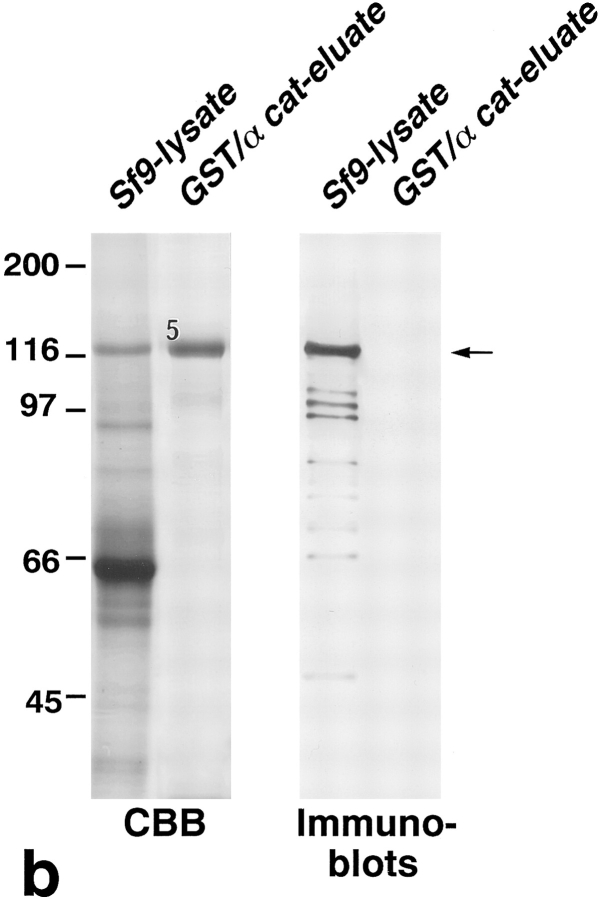
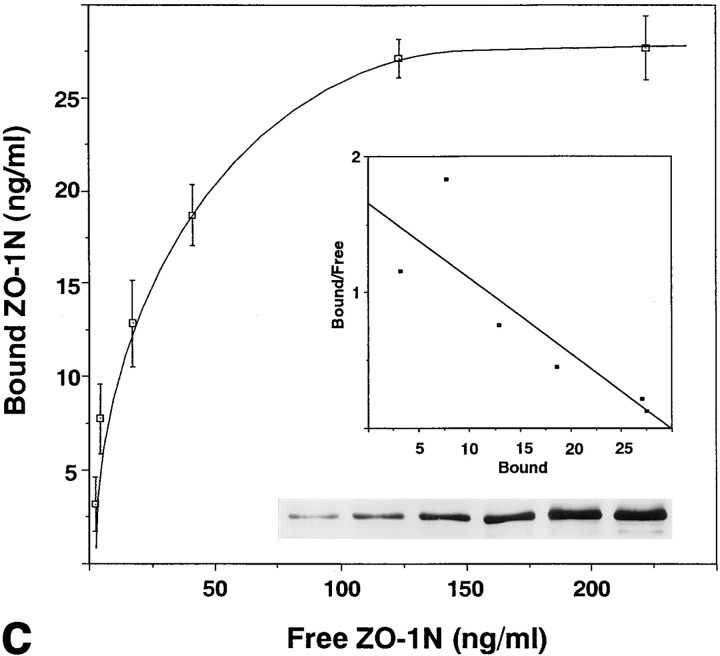
Figure 5.
Association of N-ZO-1 with α catenin in vitro. (a) GST fusion proteins with the cytoplasmic domain of occludin, the cytoplasmic domain of E-cadherin, α catenin, and β catenin, which were bound to glutathione-Sepharose beads, were incubated with the lysate of Sf9 cells expressing N-ZO-1. After washing, the proteins associated with GST fusion proteins were eluted from the beads with a buffer containing glutathione. The Sf9 cell lysate (Sf9 lysate), the eluate from GST– occludin beads (GST/Occ-eluate), the eluate from GST–E-cadherin beads (GST/Cad-eluate), the eluate from GST–α catenin beads (GST/ α cat-eluate), the eluate from GST–β catenin beads (GST/β cat-eluate), and purified GST–α catenin (GST/α cat) were separated by SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblotting with anti–ZO-1 mAb, T8-754. Although the N-ZO-1 band was not resolved from the GST–α catenin band by CBB staining, immunoblotting identified N-ZO-1 (arrowhead) in the eluate from GST–α catenin beads at the same amount as in that from GST–occludin beads (arrow), in which the N-ZO-1 band was clearly visualized by CBB staining (asterisk). N-ZO-1 was not detected in the eluates from GST–E-cadherin or GST–β catenin beads. Comparison of the CBB staining patterns between the GST–α catenin beads eluate (GST/α cat-eluate) and the purified GST–α catenin (GST/α cat) revealed that only N-ZO-1 was precipitated out from the crude Sf9 lysate by GST–α catenin, indicating the direct α catenin/N-ZO-1 interaction. 1, 2, 3, and 4 indicate the bands of GST–occludin, GST–E-cadherin, GST–α catenin, and GST–β catenin, respectively, and the other lower molecular mass bands are their degradation products. (b) GST fusion protein with α catenin, which was bound by glutathione-Sepharose beads, was incubated with the lysate of Sf9 cells expressing C-ZO-1. After washing, the proteins associated with the GST fusion protein were eluted from the beads with a buffer containing glutathione. The Sf9 cell lysate (Sf9-lysate) and the eluate from GST–α-catenin beads (GST/α cat-eluate) were separated by SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblotting with anti–C-ZO-1 mAb, T7-713. 5, the band of GST–α catenin. No specific binding was detected between GST–α-catenin and C-ZO-1 (arrow). (c) Quantitative analysis of the binding between N-ZO-1 and α catenin. Glutathione-Sepharose bead slurry containing 40 μg of GST–α catenin was incubated with the Sf9 cell lysate containing 0.012–0.6 μg of N-ZO-1. The amounts of N-ZO-1 in the Sf9 cell lysate and in each eluate (inset) were estimated as described in Materials and Methods. Each point represents the mean ± SD of triplicate determinations. The binding was saturable, and Scatchard analysis (inset) indicated that the K d was ∼0.5 nM.