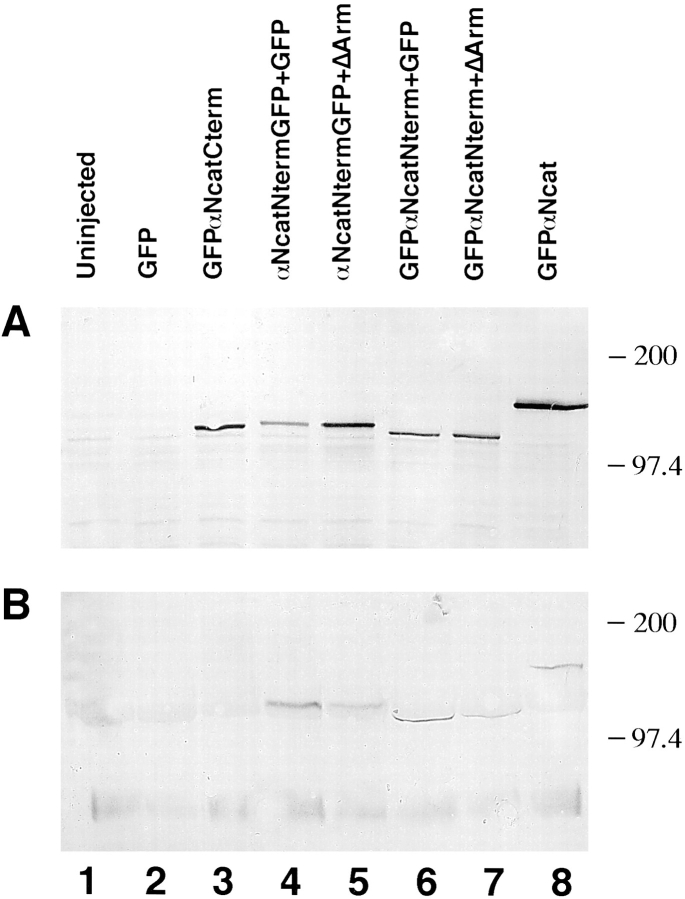
Figure 7.
Redistribution of GFPαNcatNterm and αNcatNtermGFP from the glycoprotein fraction to the soluble fraction by ΔArm. (A) Soluble fractions immunoblotted with the anti-GFP polyclonal antibody. (B) Glycoprotein fractions immunoblotted with the anti-GFP polyclonal antibody. Lanes in both cases are 1, uninjected; 2, GFP injected; 3, GFPαNcatCterm injected; 4, αNcatNtermGFP + GFP; 5, αNcatNtermGFP + ΔArm; 6, GFPαNcatNterm + GFP; 7, GFPαNcatNterm + ΔArm; 8, GFPαNcat. Note the decrease in B between lanes 4 and 5 and lanes 6 and 7, implying that ΔArm acts by binding to the α-catenin mutants, keeping them from binding to the cadherin complex. When coinjections were done, 0.3 ng of the first mRNA was coninjected with 1.2 ng of the second mRNA.