Figure 3.
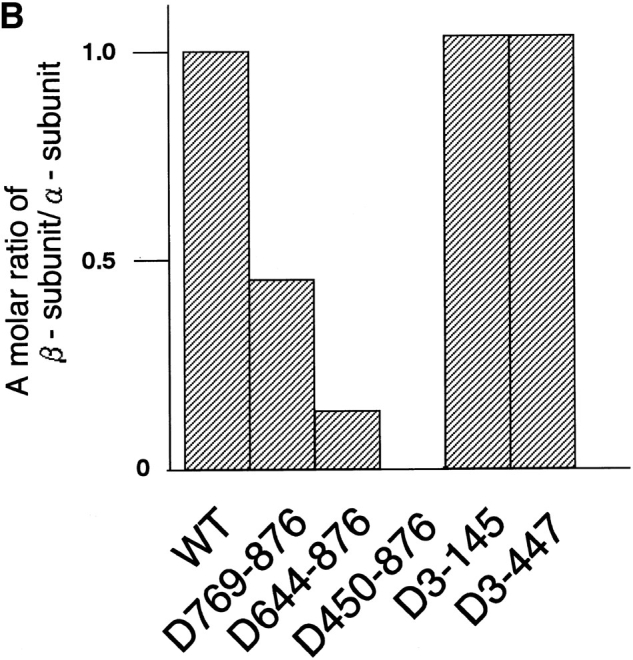
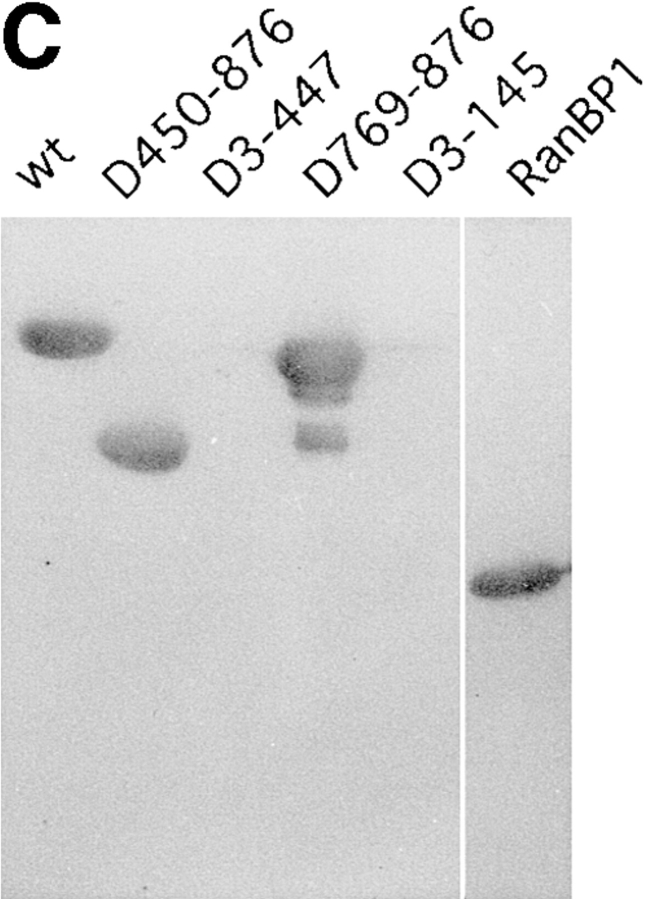
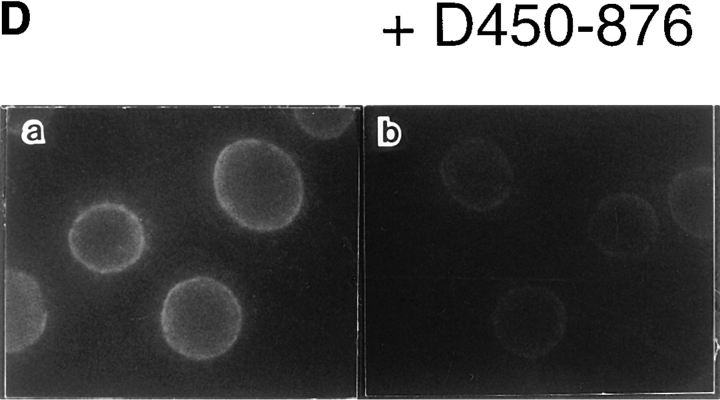
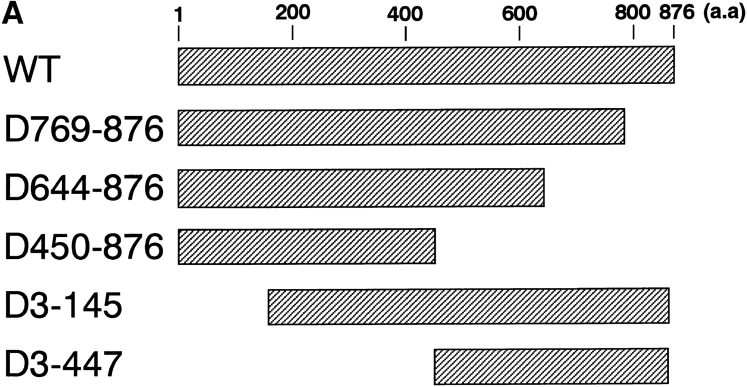
Mapping of the α-subunit-, Ran-, and NPC-binding domains of β-subunit. (A) The constructions of the deletion mutants of β-subunit. (B) α-Subunit–binding activity of deletion mutants of β-subunit. GST–β-subunit or its deletion mutants were incubated with 30 pmol GST–α-subunit and T-bBSA (0.25 mg/ ml) for 30 min at 37°C and then trapped in immobilized avidin. The bound proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE and quantified by densitometric scanning, and molar ratios of β-subunit or its deletion mutants bound to α-subunit were determined. (C) Ran-binding activity of deletion mutants of β-subunit was determined by overlay assay. 100 pmol of wild-type β-subunit and its deletions, or RanBP1, were subjected to SDS-PAGE, transferred to nitrocellulose sheet, and incubated with [γ-32P]GTP-Ran as described under experimental procedures. [γ-32P]GTP-Ran bound to the recombinant proteins were detected by autoradiography. (D) NH2-terminal portion of β-subunit competitively inhibits NPC docking of PTAC. Digitonin-permeabilized cells were incubated with 10 μl testing solution containing 12 pmol GST–β-subunit, 12 pmol GST–α-subunit, and T-APC (0.1 mg/ml) in the presence (b) or absence (a) of 144 pmol D450-876 mutant for 20 min on ice. After incubation, the cells were fixed with 3.7% formaldehyde in TB, and T-APC was detected by Axiophot microscopy (Carl Zeiss Inc.).